Simple cases
When we synthesize an aromatic product using a series of EAS reactions, the order of steps is critical for determining the regiochemistry of the product (i.e., where the groups go).
If we wish to prepare a meta-disubstituted product, we must ensure that the second EAS step is controlled by a meta-directing substituent. The same principles apply if we are synthesizing a trisubstituted product, only then we have more substituents to take into consideration.
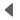
Consider a case where we want to synthesize an isomer of iodonitrobenzene, such as 1-iodo-3-nitrobenzene.

This product contains one group that is a meta director (the NO2), and another group that is an ortho/para director. Therefore if we wish to make the meta product, we must introduce the meta director first.

On the other hand, if the target is an ortho or para isomer, we must introduce the ortho/para director (the iodine) first. You should assume that ortho and para isomers can be separated in a synthesis; clearly the yield suffers as a result, but usually you have little choice in introductory aromatic synthesis.

More complex cases
Some substituents, such as nitro groups or ketones (from Friedel-Crafts acylation) direct meta, but they are often reduced to produce ortho/para directors (NH2 and alkyl groups, respectively). In this case, we can change the isomer we get by performing the reduction either before or after the next EAS reaction. Consider a synthesis of 1-chloro-3-ethylbenzene (the meta isomer) from benzene, where we want to ensure that we hold off on reducing the C=O until after we have introduced the chlorine:

On the other hand, if we want to synthesize 1-chloro-2-ethyl-benzene, the ortho isomer, we should reduce before the chlorination step:

Alternatively, since Cl is also an ortho/para director, we could do the chlorine first, and then the Friedel-Crafts acylation:

Either of these last two would be expected to work well, and would be given full marks on an exam. In practice, it is known that the second of these methods gives a lower percentage of the ortho isomer (and more para), so it would probably be better to introduce an ethyl group and then the chlorine. This matters for an industrial process, but in an introductory course like this, either answer will be treated as equally correct.