


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 17-4-2019
Date: 30-10-2020
Date: 13-4-2019
|
Phun with the pH Scale
The acidity of a solution is related to the concentration of the hydronium ion in the solution: The more acidic the solution is, the higher the concentration. In other words, a solution in which the [H3O+] equals 1.0 × 10–2 is more acidic than a solution in which the [H3O+] equals 1.0 × 10–7.
Scientists developed the pH scale, a scale based on the [H3O+], to more easily tell, at a glance, the relative acidity of a solution. The pH is defined as the negative logarithm (abbreviated as log) of [H3O+]. Mathematically, it looks like this:
pH = – log [H3O+]
In pure water, the [H3O+] equals 1.0 × 10–7, based on the water dissociation constant, Kw (see “Acting as either an acid or a base: Amphoteric water,” earlier in this chapter. Using this mathematical relationship, you can calculate the pH of pure water:
pH = – log [H3O+]
pH = – log [1.0 × 10–7]
pH = – [–7]
pH = 7
The pH of pure water is 7. Chemists call this point on the pH scale neutral. A solution is acidic if it has a larger [H3O+] than water and a smaller pH value than 7. A basic solution has a smaller [H3O+] than water and a larger pH value than 7. The pH scale really has no end. You can have a solution of pH that registers less than 0. (A 10 M HCl solution, for example, has a pH of –1.) However, the 0 to 14 range is a convenient range to use for weak acids and bases and for dilute solutions of strong acids and bases. Figure 1-1 shows the pH scale. The [H3O+] of a 2.0 M acetic acid solution is 6.0 × 10–3. Looking at the pH scale, you see that this solution is acidic. Now calculate the pH of this solution:
pH = – log [H3O+]
pH = – log [6.0 × 10–3]
pH = – [–2.22]
pH = 2.22
The pOH is the negative logarithm of the [OH–], and it can be useful in calculating the pH of a solution. You can calculate the pOH of a solution just like the pH by taking the negative log of the hydroxide ion concentration. If you use the Kw expression (which enables you to calculate the [H3O+] if you have the [OH–]; see the section “Acting as either an acid or base: Amphoteric water”) and take the negative log of both sides, you get 14 = pH + pOH. This equation makes it easy to go from pOH to pH.
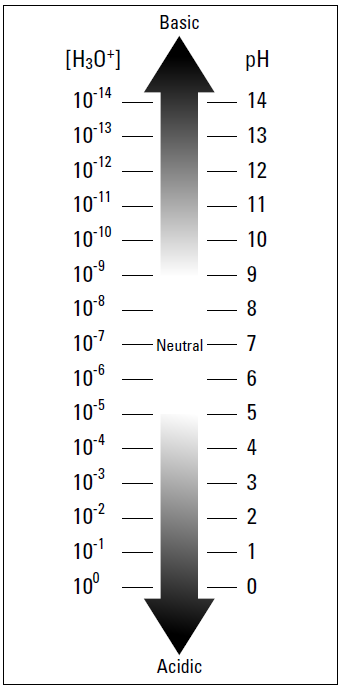
Figure 1-1: The pH scale.
Just as you can you convert from [H3O+] to pH, you can also go from pH to [H3O+]. To do this, you use what’s called the antilog relationship, which is [H3O+] = 10–pH Human blood, for example, has a pH of 7.3. Here’s how you calculate the [H3O+] from the pH of blood:
[H3O+] = 10–pH
[H3O+] = 10–7.3
[H3O+] = 5.01 × 10–8
You can use the same procedure to calculate the [OH–] from the pOH.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي ينظّم ندوة حوارية حول مفهوم العولمة الرقمية في بابل
|
|
|