


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 12-1-2017
Date: 17-6-2019
Date: 2-2-2018
|
AX2E Molecules: SO2 ( Three Electron Groups )
1. The central atom, sulfur, has 6 valence electrons, as does each oxygen atom. With 18 valence electrons, the Lewis electron structure is shown below.
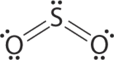
2. There are three electron groups around the central atom, two double bonds and one lone pair. We initially place the groups in a trigonal planar arrangement to minimize repulsions.
3. There are two bonding pairs and one lone pair, so the structure is designated as AX2E. This designation has a total of three electron pairs, two X and one E. Because a lone pair is not shared by two nuclei, it occupies more space near the central atom than a bonding pair . Thus bonding pairs and lone pairs repel each other electrostatically in the order BP–BP < LP–BP < LP–LP. In SO2, we have one BP–BP interaction and two LP–BP interactions.
4. The molecular geometry is described only by the positions of the nuclei, not by the positions of the lone pairs. Thus with two nuclei and one lone pair the shape is bent, or V shaped, which can be viewed as a trigonal planar arrangement with a missing vertex. The O-S-O bond angle is expected to be less than 120° because of the extra space taken up by the lone pair.

Figure 1.1: The Difference in the Space Occupied by a Lone Pair of Electrons and by a Bonding Pair
As with SO2, this composite model of electron distribution and negative electrostatic potential in ammonia shows that a lone pair of electrons occupies a larger region of space around the nitrogen atom than does a bonding pair of electrons that is shared with a hydrogen atom.
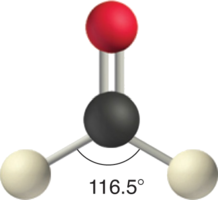
Like lone pairs of electrons, multiple bonds occupy more space around the central atom than a single bond, which can cause other bond angles to be somewhat smaller than expected. This is because a multiple bond has a higher electron density than a single bond, so its electrons occupy more space than those of a single bond. For example, in a molecule such as CH2O (AX3), whose structure is shown below, the double bond repels the single bonds more strongly than the single bonds repel each other. This causes a deviation from ideal geometry (an H–C–H bond angle of 116.5° rather than 120°).



|
|
|
|
دراسة تحدد أفضل 4 وجبات صحية.. وأخطرها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
استمرار توافد مختلف الشخصيات والوفود لتهنئة الأمين العام للعتبة العباسية بمناسبة إعادة تعيينه
|
|
|