


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 11-8-2019
Date: 13-8-2018
Date: 13-8-2018
|
Group Frequencies
Detailed information about the infrared absorptions observed for various bonded atoms and groups is usually presented in tabular form. The following table provides a collection of such data for the most common functional groups. Following the color scheme of the chart, stretching absorptions are listed in the blue-shaded section and bending absorptions in the green shaded part. More detailed descriptions for certain groups (e.g. alkenes, arenes, alcohols, amines & carbonyl compounds) may be viewed by clicking on the functional class name. Since most organic compounds have C-H bonds, a useful rule is that absorption in the 2850 to 3000 cm-1 is due to sp3 C-H stretching; whereas, absorption above 3000 cm-1 is from sp2 C-H stretching or sp C-H stretching if it is near 3300 cm-1.
|
Stretching Vibrations |
Bending Vibrations |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Functional Class |
Range (cm-1) |
Intensity |
Assignment |
Range (cm-1) |
Intensity |
Assignment |
|
Alkanes |
2850-3000 | str | CH3, CH2 & CH 2 or 3 bands |
1350-1470 1370-1390 720-725 |
med med wk |
CH2 & CH3 deformation CH3 deformation CH2 rocking |
|
Alkenes |
3020-3100 1630-1680 1900-2000 |
med var str |
=C-H & =CH2 (usually sharp) C=C (symmetry reduces intensity) C=C asymmetric stretch |
880-995 780-850 675-730 |
str med med |
=C-H & =CH2 (out-of-plane bending) cis-RCH=CHR |
|
Alkynes |
3300 2100-2250 |
str var |
C-H (usually sharp) C≡C (symmetry reduces intensity) |
600-700 | str | C-H deformation |
|
Arenes |
3030 1600 & 1500 |
var med-wk |
C-H (may be several bands) C=C (in ring) (2 bands) (3 if conjugated) |
690-900 | str-med | C-H bending & ring puckering |
|
Alcohols & Phenols |
3580-3650 3200-3550 970-1250 |
var str str |
O-H (free), usually sharp O-H (H-bonded), usually broad C-O |
1330-1430 650-770 |
med var-wk |
O-H bending (in-plane) O-H bend (out-of-plane) |
|
Amines |
3400-3500 (dil. soln.) 3300-3400 (dil. soln.) 1000-1250 |
wk wk med |
N-H (1°-amines), 2 bands N-H (2°-amines) C-N |
1550-1650 660-900 |
med-str var |
NH2 scissoring (1°-amines) NH2 & N-H wagging (shifts on H-bonding) |
|
Aldehydes & Ketones |
2690-2840(2 bands) 1690 1675 1745 1780 |
med str str str str str str |
C-H (aldehyde C-H) C=O (saturated aldehyde) C=O (saturated ketone) aryl ketone α, β-unsaturation cyclopentanone cyclobutanone |
1350-1360 1400-1450 1100 |
str str med |
α-CH3 bending α-CH2 bending C-C-C bending |
|
Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives |
2500-3300 (acids) overlap C-H 1785-1815 ( acyl halides) 1750 & 1820 (anhydrides) 1040-1100 1735-1750 (esters) 1000-1300 1630-1695(amides) |
str str med-str str str str str str str |
O-H (very broad) C=O (H-bonded) O-C (sometimes 2-peaks) C=O C=O (2-bands) O-C C=O O-C (2-bands) C=O (amide I band) |
1395-1440 1590-1650 1500-1560 |
med med med |
C-O-H bending N-H (1¡-amide) II band N-H (2¡-amide) II band |
|
Nitriles |
2240-2260 2100-2270 |
med med |
C≡N (sharp) -N=C=O, -N=C=S -N=C=N-, -N3, C=C=O |
|||
To illustrate the usefulness of infrared absorption spectra, examples for five C4H8O isomers are presented below their corresponding structural formulas. The five spectra may be examined in turn by clicking the "Toggle Spectra" button. Try to associate each spectrum (A - E) with one of the isomers in the row above it. When you have made assignments check your answers by clicking on the structure or name of each isomer.
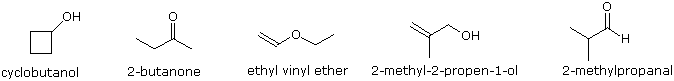
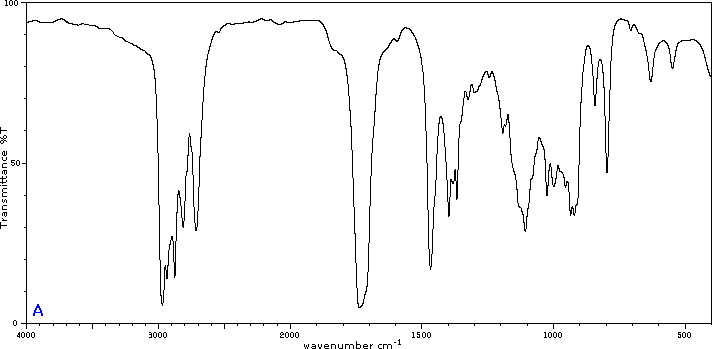
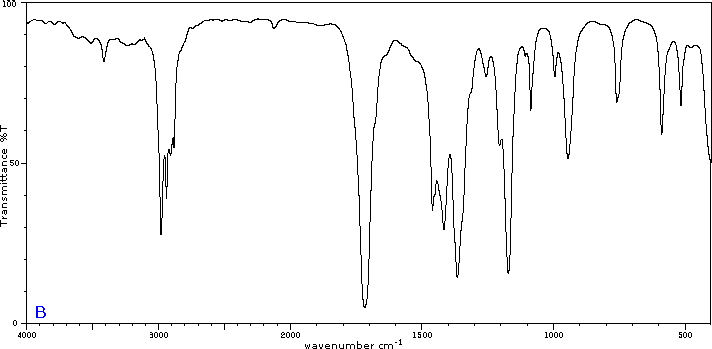
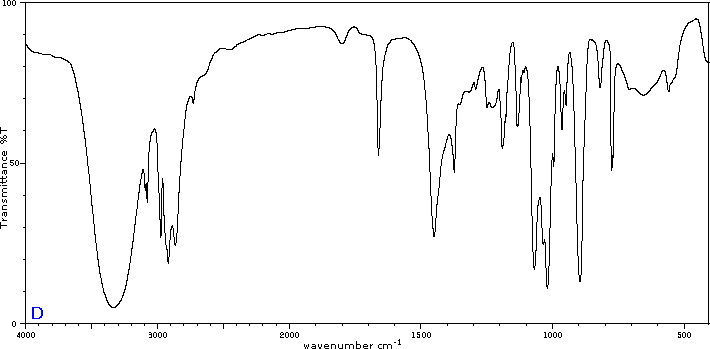
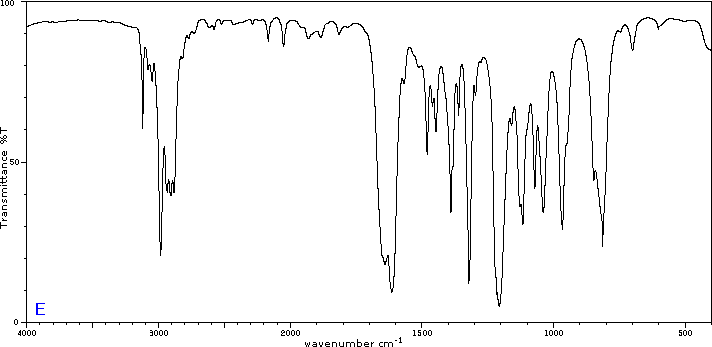



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
بالصور: معهد نور الإمام الحسين (ع) للمكفوفين وضعاف البصر التابع للعتبة الحسينية.. جهود كبيرة وخدمات متعددة
|
|
|