

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
1H Chemical Shifts of Methanol in Selected Solvents
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
13-8-2018
1707
1H Chemical Shifts of Methanol in Selected Solvents
| Solvent | CDCl3 | CD3COCD3 | CD3SOCD3 | CD3C≡N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH3–O–H CH3 O–H |
3.40 1.10 |
3.31 3.12 |
3.16 4.01 |
3.28 2.16 |
The solvent effect shown above suggests a useful diagnostic procedure for characterizing the OH resonance signals from alcohol samples. For example, a solution of ethanol in chloroform-d displays the spectrum shown on the left below, especially if traces of HCl are present (otherwise broadening of the OH and CH2 signals occurs). Note that the chemical shift of the OH signal (red) is less than that of the methylene group (blue), and no coupling of the OH proton is apparent. The vicinal coupling (J = 7 Hz) of the methyl and methylene hydrogens is typical of ethyl groups. In DMSO-d6 solution small changes of chemical shift are seen for the methyl and methylene group hydrogens, but a dramatic downfield shift of the hydroxyl signal takes place because of hydrogen bonding. Coupling of the OH proton to the adjacent methylene group is evident, and both the coupling constants can be measured. Because the coupling constants are different, the methylene signal pattern is an overlapping doublet of quartets (eight distinct lines) rather than a quintet. Note that residual hydrogens in the solvent give a small broad signal near δ 2.5 ppm.
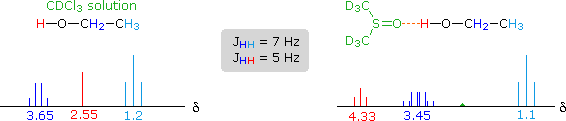
For many alcohols in dilute chloroform-d solution, the hydroxyl resonance signal is often broad and obscured by other signals in the δ 1.5 to 3.0 region. The simple technique of using DMSO-d6 as a solvent, not only shifts this signal to a lower field, but permits 1°-, 2 °- & 3 °-alcohols to be distinguished. Thus, the hydroxyl proton of 2-propanol generates a doublet at δ 4.35 ppm, and the corresponding signal from 2-methyl-2-propanol is a singlet at δ 4.2 ppm. The more acidic OH protons of phenols are similarly shifted – from δ 4 to 7 in chloroform-d to δ 8.5 to 9.5 in DMSO-d6.
 الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
الاكثر قراءة في التشخيص العضوي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















