

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Factors Influencing Carbocation Stability
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
20-7-2018
2870
Factors Influencing Carbocation Stability
Carbocation intermediates, sometimes called carbonium ions, have been proposed or identified as important species in reactions ranging from electrophilic addition to alkenes, to unimolecular solvolysis of alkyl halides. The relative stability of these cationic intermediates varies markedly with the presence of substituents on the trivalent charged carbon atom, in a fashion that has led useful empirical rules for predicting reaction selectivity (summarized elsewhere). This stability order for simple alkyl alkenyl and aryl substituted carbocations is repeated below, followed by a table of supportive data.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
A few carbocations, such as tropylium and trityl (triphenylcarbenium) shown on the right, are sufficiently stable to form isolable salts with poorly nucleophilic anions, such as tetrafluoroborate (BF4(–) ). However, most carbocations are unstable and very reactive under normal laboratory conditions, so conventional studies of all but the most stable of these species have not been possible.
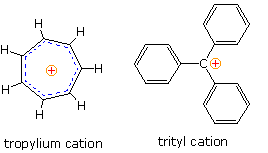
Nevertheless, gas phase ionization energies of alkyl chlorides, hydride affinity measurements (gas phase), molecular orbital calculations, and low temperature nmr examination of ionized alkyl halides in mixed solvents composed of SbF5, SO2, SO2F2 & SO2FCl. (referred to as "super acids") have confirmed the qualitative relationship shown above. At low temperatures, 1H and 13C nmr spectra of (CH3)3C(+) and (CH3)2CH(+) were obtained and interpreted. The charged tricoordinate carbon atom exhibited a 13C signal over 300ppm downfield from TMS.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















