


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 14-8-2016
Date: 3-9-2016
Date: 6-9-2016
|
Lowest Mode of Rectangular Wave Guide
Consider a rectangular wave guide, infinitely long in the direction, with a width (x direction) of a and a height (y direction) of b (a > b) (see Figure 1.1). The walls are perfect conductors.
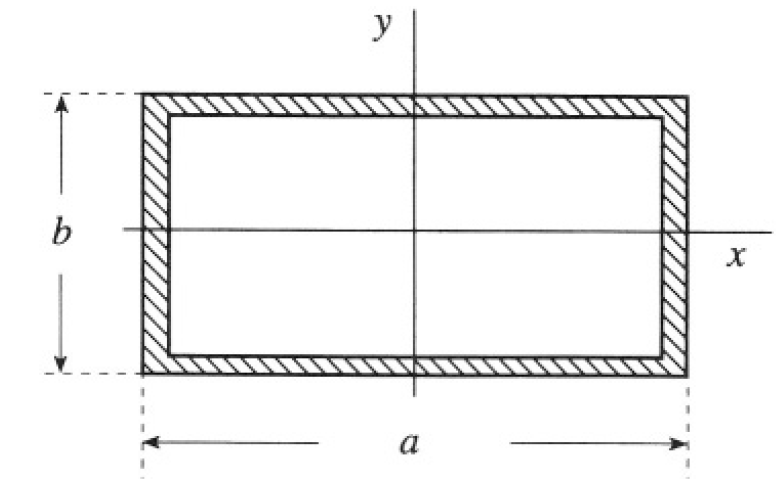
Figure 1.1
a) What are the boundary conditions on the components of B and E at the walls?
b) Write the wave equation which describes the E and B fields of the lowest mode.
Hint: The lowest mode has the electric field in the y direction only.
c) For the lowest mode that can propagate, find the phase velocity and the group velocity.
d) The possible modes of propagation separate naturally into two classes. What are these two classes and how do they differ physically?
SOLUTION
a) Because the walls are perfectly conducting, we have for E and B the boundary conditions

where n is normal to the wall, or in terms of Ez (Bz) (z is the direction of wave propagation)
 (1)
(1)
b) Starting from the sourceless Maxwell equations in vacuum
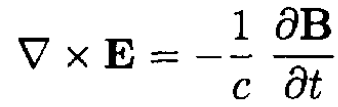 (2)
(2)
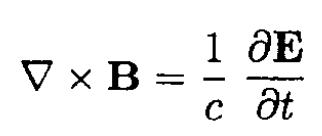 (3)
(3)
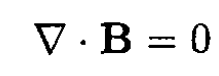 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
and substituting E (r, t) = E (r) exp (-ωt) (same for B), we obtain
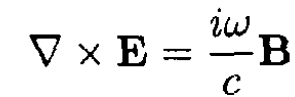 (6)
(6)
 (7)
(7)
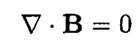 (8)
(8)
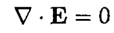 (9)
(9)
The field dependence on may be written in the form f(z) = exp [i (kz – ωt)], where k is the wave vector for the wave transmitted in the z direction. Using the fact that the electric field of the lowest mode is in the y direction only, we have, from (6)–( 7),
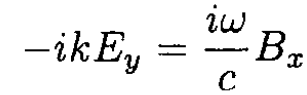 (10)
(10)
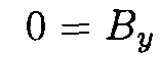 (11)
(11)
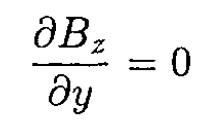 (12)
(12)
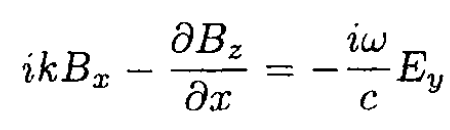 (13)
(13)
From (12), Bz = B (x) exp (ikz), and substituting (10) into (13), we obtain
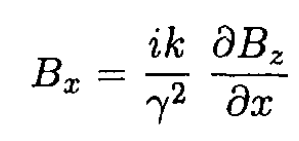 (14)
(14)
 (15)
(15)
where
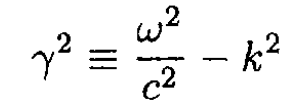 (16)
(16)
Using 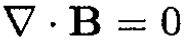 and Bx from (14), we get a differential equation for Bz
and Bx from (14), we get a differential equation for Bz
 (17)
(17)
or
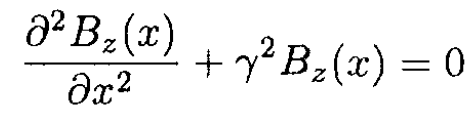 (18)
(18)
The solution of this equation satisfying the boundary conditions
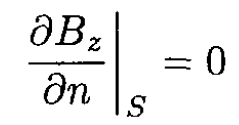
is Bz = B0 cos γx with γ = π/a. So the field in the wave guide in this mode from (14)– (15)
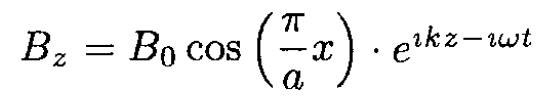 (19)
(19)
 (20)
(20)
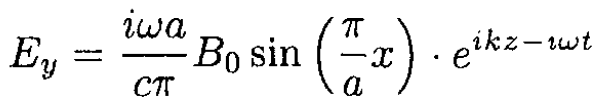 (21)
(21)
c) The dispersion relation for the lowest mode is found from (16):
 (22)
(22)
The phase velocity v is
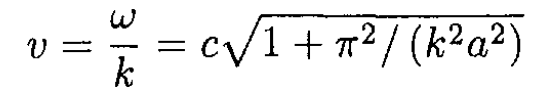 (23)
(23)
The group velocity u is
 (24)
(24)
d) The waves propagating in the wave guides can be divided into two classes: TE (transverse electric, Ez = 0) as is the case in this problem, and TM (transverse magnetic, Bz = 0).



|
|
|
|
دور في الحماية من السرطان.. يجب تناول لبن الزبادي يوميا
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العلماء الروس يطورون مسيرة لمراقبة حرائق الغابات
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ضمن أسبوع الإرشاد النفسي.. جامعة العميد تُقيم أنشطةً ثقافية وتطويرية لطلبتها
|
|
|