


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 2-5-2021
Date: 5-5-2016
Date: 7-12-2015
|
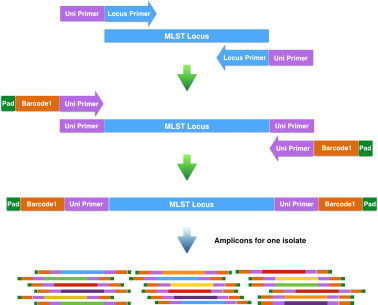
Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
The MLST technique is well described. There are three elements to the design of a new MLST system: the choice of the isolates to be used in the initial evaluation, the choice of the genetic loci to be characterised and the design of primers for gene amplification and nucleotide sequence determination.
It is advisable to assemble a diverse isolate collection on the basis of existing typing information or epidemiological data. This should comprise around 100 isolates (95 is a good number if high-throughput sequencing in 96-well microtitre plates is to be done) to ensure that the primers developed will be applicable to as many isolates as possible and to establish the levels of diversity present at each of the loci to be examined. Furthermore, the collection will ideally be representative of the bacterial population, rather than comprising a subset, such as human disease isolates.
Housekeeping genes, flanked by genes of similar function, are good targets for MLST and the availability of complete genome sequences has greatly facilitated the identification of candidate loci. Experience with several bacterial species has indicated that PCR fragments of housekeeping genes around 450 bp are suitable for MLST and a nested strategy is highly recommended for sequencing. The great advantage of MLST is that sequence data are unambiguous and the allelic profiles of isolates can easily be compared with those in a large central database via the Internet (in contrast to most typing procedures, which involve comparing DNA fragment sizes on gels). Allelic profiles can also be obtained from clinical material by PCR amplification of housekeeping loci directly from patient samples. Thus isolates can be precisely characterised even when they cannot be cultured from clinical material. MLST can effectively distinguish strains that possess high degrees of homology within the compared gene sequences. This technique is not as laborious as PFGE and it provides balance between sequence-based resolution and technical feasibility.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|