


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 2-2-2019
Date: 1-1-2017
Date: 1-1-2017
|
The effects of radiation depend on the type, energy, and location of the radiation source, and the length of exposure. As shown in Figure 1 , the average person is exposed to background radiation, including cosmic rays from the sun and radon from uranium in the ground (see the Chemistry in Everyday Life feature on Radon Exposure); radiation from medical exposure, including CAT scans, radioisotope tests, X-rays, and so on; and small amounts of radiation from other human activities, such as airplane flights (which are bombarded by increased numbers of cosmic rays in the upper atmosphere), radioactivity from consumer products, and a variety of radionuclides that enter our bodies when we breathe (for example, carbon-14) or through the food chain (for example, potassium-40, strontium-90, and iodine-131).
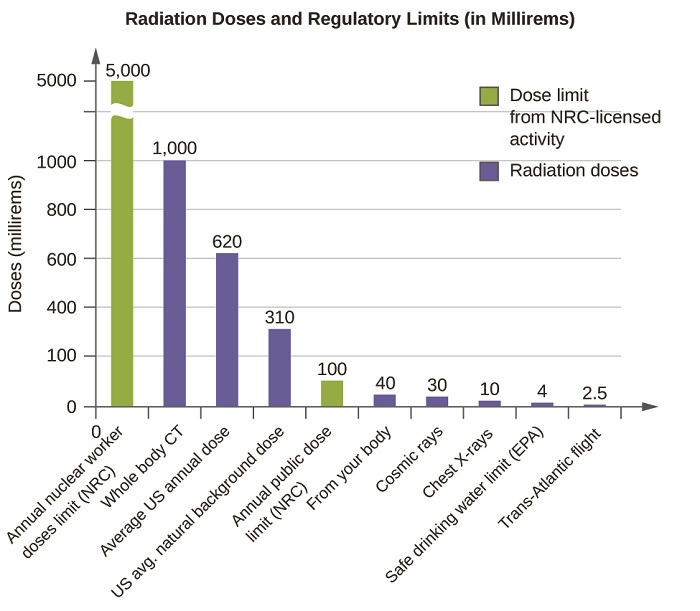
Figure 1 : The total annual radiation exposure for a person in the US is about 620 mrem. The various sources and their relative amounts are shown in this bar graph. (source: U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission).
A short-term, sudden dose of a large amount of radiation can cause a wide range of health effects, from changes in blood chemistry to death. Short-term exposure to tens of rems of radiation will likely cause very noticeable symptoms or illness; a dose of about 500 rems is estimated to have a 50% probability of causing the death of the victim within 30 days of exposure. Exposure to radioactive emissions has a cumulative effect on the body during a person’s lifetime, which is another reason why it is important to avoid any unnecessary exposure to radiation. Health effects of short-term exposure to radiation are shown in Table 1.
| Exposure (rem) | Health Effect | Time to Onset (without treatment) |
|---|---|---|
| 5–10 | changes in blood chemistry | — |
| 50 | nausea | hours |
| 55 | fatigue | — |
| 70 | vomiting | — |
| 75 | hair loss | 2–3 weeks |
| 90 | diarrhea | — |
| 100 | hemorrhage | — |
| 400 | possible death | within 2 months |
| 1000 | destruction of intestinal lining | — |
| internal bleeding | — | |
| death | 1–2 weeks | |
| 2000 | damage to central nervous system | — |
| loss of consciousness; | minutes | |
| death | hours to days |
It is impossible to avoid some exposure to ionizing radiation. We are constantly exposed to background radiation from a variety of natural sources, including cosmic radiation, rocks, medical procedures, consumer products, and even our own atoms. We can minimize our exposure by blocking or shielding the radiation, moving farther from the source, and limiting the time of exposure.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|