


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 10-12-2019
Date: 10-12-2019
Date: 10-12-2019
|
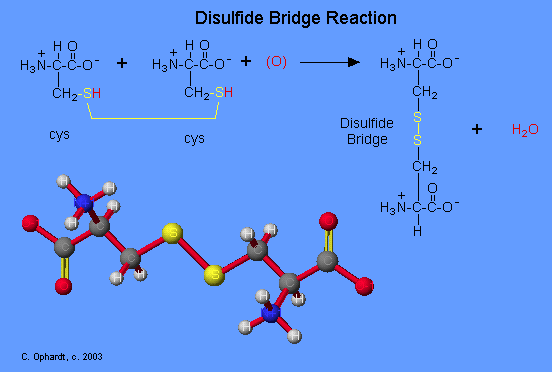
The amino acid cysteine undergoes oxidation and reduction reactions involving the -SH (sulfhydryl group). The oxidation of two sulfhydryl groups results in the formation of a disulfide bond by the removal of two hydrogens. The oxidation of two cysteine amino acids is shown in the graphic. An unspecified oxidizing agent (O) provides an oxygen which reacts with the hydrogen (red) on the -SH group to form water. The sulfurs (yellow) join to make the disulfide bridge. This is an important bond to recognize in protein tertiary structure. The reduction of a disulfide bond is the opposite reaction which again leads to two separate cysteine molecules. Remember that reduction is the addition of hydrogen.
Cysteine residues in the the peptide chain can form a loop buy forming the disulfide bond (—S—S—), while cysteine residues in different peptide chains can actually link what were otherwise separate chains. Insulin was the first protein whose amino acid sequence was determined. This pioneering work, completed in 1953 after some 10 years of effort, earned a Nobel Prize for British biochemist Frederick Sanger (born 1918). He found the primary structure to comprise of two chains linked by two cysteine disulfide bridges. Also note the first peptide chain possesses an internal loop.
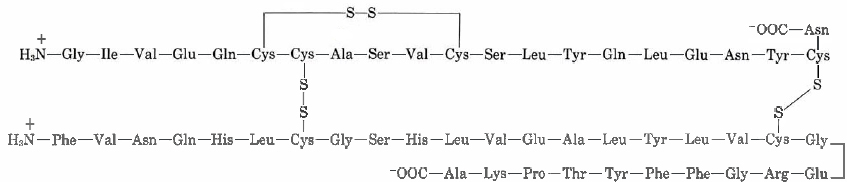
Insulin



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
سماحة السيد الصافي يؤكد ضرورة تعريف المجتمعات بأهمية مبادئ أهل البيت (عليهم السلام) في إيجاد حلول للمشاكل الاجتماعية
|
|
|