


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 26-2-2016
Date: 20-7-2018
Date: 29-7-2018
|
It is possible to dissolve ionic compounds in organic solvents using crown ethers. Cyclic polyether with four or more oxygen atoms separated by two or three carbon atoms. All crown ethers have a central cavity that can accommodate a metal ion coordinated to the ring of oxygen atoms., cyclic compounds with the general formula (OCH2CH2)n. Crown ethers are named using both the total number of atoms in the ring and the number of oxygen atoms. Thus 18-crown-6 is an 18-membered ring with six oxygen atoms (part (a) in Figure 1.1 ). The cavity in the center of the crown ether molecule is lined with oxygen atoms and is large enough to be occupied by a cation, such as K+. The cation is stabilized by interacting with lone pairs of electrons on the surrounding oxygen atoms. Thus crown ethers solvate cations inside a hydrophilic cavity, whereas the outer shell, consisting of C–H bonds, is hydrophobic. Crown ethers are useful for dissolving ionic substances such as KMnO4 in organic solvents such as isopropanol [(CH3)2CHOH] (Figure 1.1). The availability of crown ethers with cavities of different sizes allows specific cations to be solvated with a high degree of selectivity.
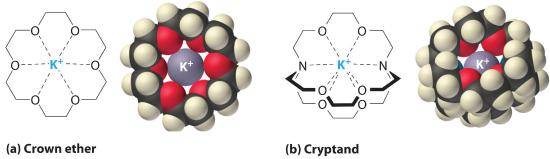
Figure 1.1: Crown Ethers and Cryptands (a) The potassium complex of the crown ether 18-crown-6. Note how the cation is nestled within the central cavity of the molecule and interacts with lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atoms. (b) The potassium complex of 2,2,2-cryptand, showing how the cation is almost hidden by the cryptand. Cryptands solvate cations via lone pairs of electrons on both oxygen and nitrogen atoms.
Cryptands (from the Greek kryptós, meaning “hidden”) are compounds that can completely surround a cation with lone pairs of electrons on oxygen and nitrogen atoms (Figure 1.1b). The number in the name of the cryptand is the number of oxygen atoms in each strand of the molecule. Like crown ethers, cryptands can be used to prepare solutions of ionic compounds in solvents that are otherwise too nonpolar to dissolve them.
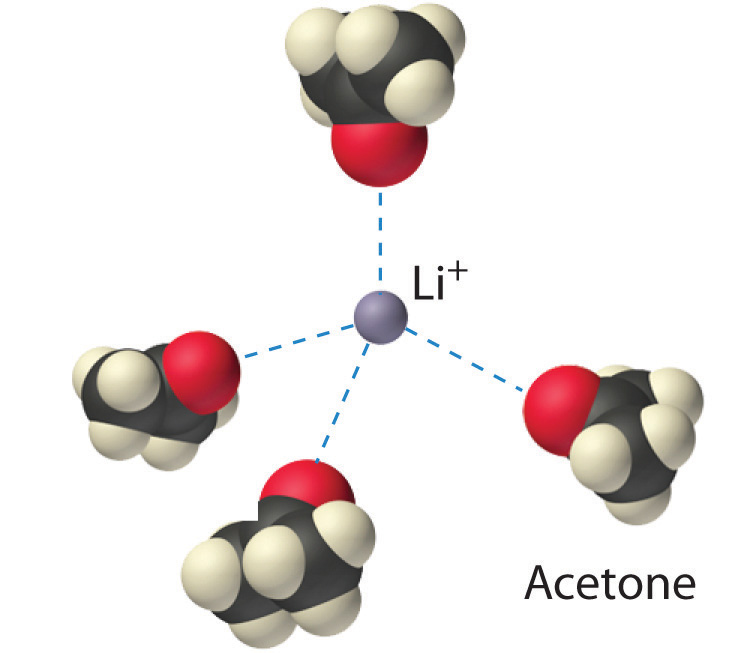
Figure 1.3: Ion–Dipole Interactions in the Solvation of Li+ Ions by Acetone, a Polar Solvent



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|