


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 28-6-2019
Date: 16-9-2019
Date: 28-7-2018
|
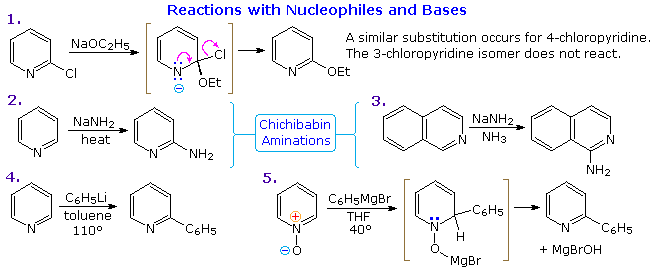
Other Reactions of Pyridine
Thanks to the nitrogen in the ring, pyridine compounds undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions more easily than equivalent benzene derivatives. In the following diagram, reaction 1 illustrates displacement of a 2-chloro substituent by ethoxide anion. The addition-elimination mechanism shown for this reaction is helped by nitrogen's ability to support a negative charge. A similar intermediate may be written for substitution of a 4-halopyridine, but substitution at the 3-position is prohibited by the the failure to create an intermediate of this kind. The two Chichibabin aminations in reactions 2 and 3 are remarkable in that the leaving anion is hydride (or an equivalent). Hydrogen is often evolved in the course of these reactions. In accord with this mechanism, quinoline is aminated at both C-2 and C-4.
Addition of strong nucleophiles to N-oxide derivatives of pyridine proceed more rapidly than to pyridine itself, as demonstrated by reactions 4 and 5. The dihydro-pyridine intermediate easily loses water or its equivalent by elimination of the –OM substituent on nitrogen.
By clicking on the above diagram, five additional examples of base or nucleophile reactions with substituted pyridine will be displayed. Because the pyridine ring (and to a greater degree the N-oxide ring) can support a negative charge, alkyl substituents in the 2- and 4-locations are activated in the same fashion as by a carbonyl group. Reactions 6 and 7 show alkylation and condensation reactions resulting from this activation. Reaction 8 is an example of N-alkylpyridone formation by hydroxide addition to an N-alkyl pyridinium cation, followed by mild oxidation. Birch reduction converts pyridines to dihydropyridines that are bis-enamines and may be hydrolyzed to 1,5-dicarbonyl compounds. Pyridinium salts undergo a one electron transfer to generate remarkably stable free radicals. The example shown in reaction 9 is a stable (in the absence of oxygen), distillable green liquid. Although 3-halopyridines do not undergo addition-elimination substitution reactions as do their 2- and 4-isomers, the strong base sodium amide effects amination by way of a pyridyne intermediate. This is illustrated by reaction 10. It is interesting that 3-pyridyne is formed in preference to 2-pyridyne. The latter is formed if C-4 is occupied by an alkyl substituent. The pyridyne intermediate is similar to benzyne.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
عقد جلسة حوارية عن ضحايا جرائم التطرف ضمن فعاليات اليوم الثاني لمؤتمر ذاكرة الألم
|
|
|