


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 7-8-2019
Date: 10-8-2018
Date: 12-1-2022
|
The fragmentation of molecular ions into an assortment of fragment ions is a mixed blessing. The nature of the fragments often provides a clue to the molecular structure, but if the molecular ion has a lifetime of less than a few microseconds it will not survive long enough to be observed. Without a molecular ion peak as a reference, the difficulty of interpreting a mass spectrum increases markedly. Fortunately, most organic compounds give mass spectra that include a molecular ion, and those that do not often respond successfully to the use of milder ionization conditions. Among simple organic compounds, the most stable molecular ions are those from aromatic rings, other conjugated pi-electron systems and cycloalkanes. Alcohols, ethers and highly branched alkanes generally show the greatest tendency toward fragmentation.
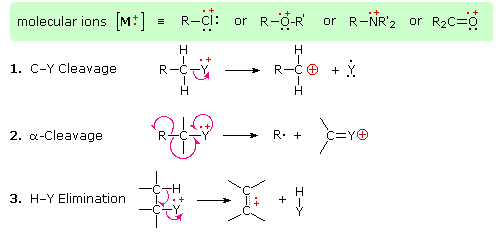
The presence of a functional group, particularly one having a heteroatom Y with non-bonding valence electrons (Y = N, O, S, X etc.), can dramatically alter the fragmentation pattern of a compound. This influence is thought to occur because of a "localization" of the radical cation component of the molecular ion on the heteroatom. After all, it is easier to remove (ionize) a non-bonding electron than one that is part of a covalent bond. By localizing the reactive moiety, certain fragmentation processes will be favored. These are summarized in the following diagram, where the green shaded box at the top displays examples of such "localized" molecular ions. The first two fragmentation paths lead to even-electron ions, and the elimination (path #3) gives an odd-electron ion. Note the use of different curved arrows to show single electron shifts compared with electron pair shifts.
3-Pentanol shows three significant fragment ions. Alpha-fragmentation (loss of an ethyl radical) forms the m/z=59 base peak. Loss of water from this gives a m/z=41 fragment, and loss of ethene from m/z=59 gives a m/z=31 fragment.



|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ملاكات العتبة العباسية المقدسة تُنهي أعمال غسل حرم مرقد أبي الفضل العباس (عليه السلام) وفرشه
|
|
|