


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 6-1-2020
Date: 6-1-2020
Date: 3-1-2020
|
Let's look at an actual 1H-NMR plot for methyl acetate. Just as in IR and UV-vis spectroscopy, the vertical axis corresponds to intensity of absorbance, the horizontal axis to frequency (typically the vertical axis is not shown in an NMR spectrum).
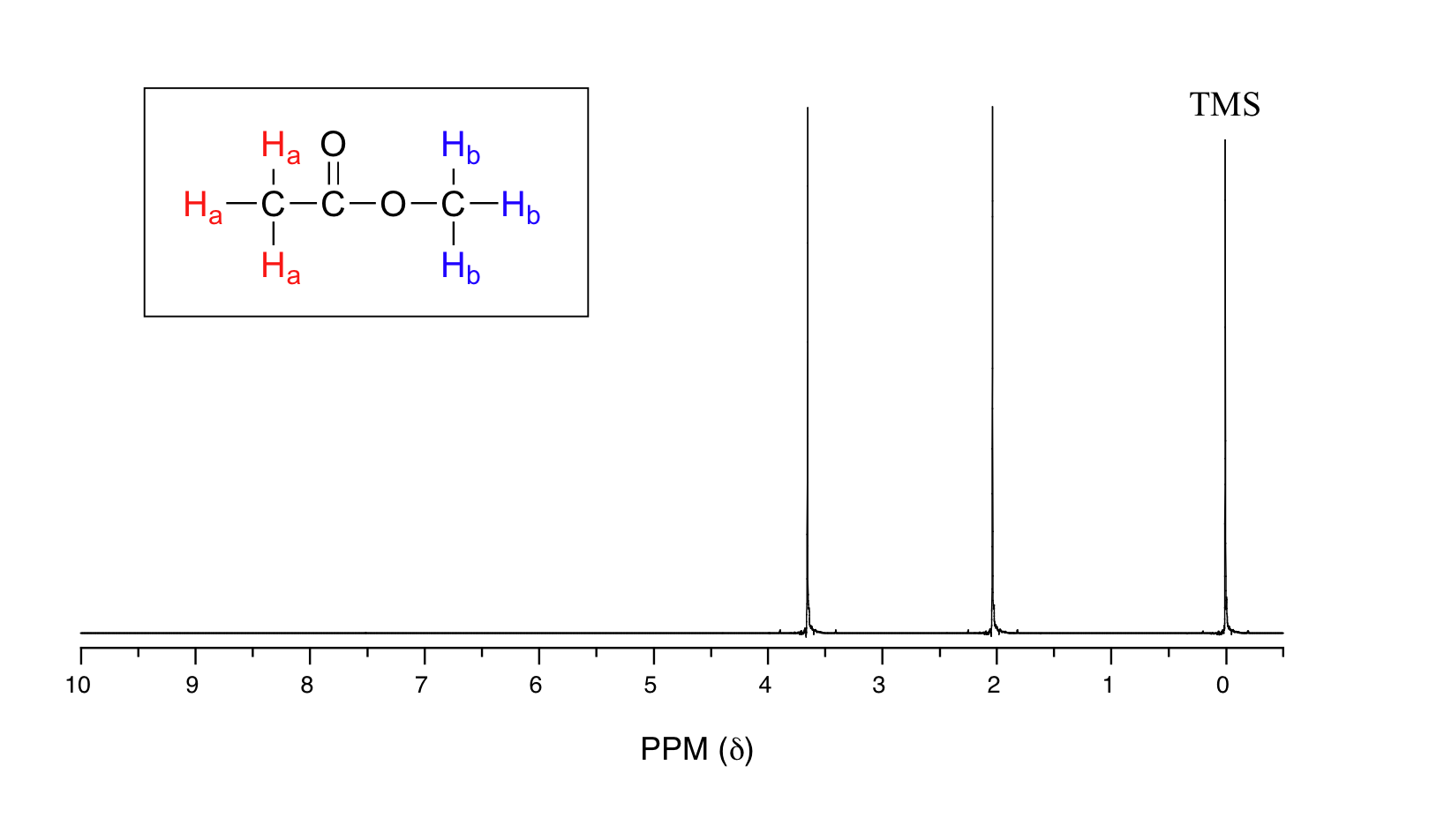
We see three absorbance signals: two of these correspond to Ha and Hb, while the peak at the far right of the spectrum corresponds to the 12 chemically equivalent protons in tetramethylsilane (TMS), a standard reference compound that was added to our sample.

You may be wondering about a few things at this point - why is TMS necessary, and what is the meaning of the `ppm (δ)` label on the horizontal axis? Shouldn't the frequency units be in Hz? Keep in mind that NMR instruments of many different applied field strengths are used in organic chemistry laboratories, and that the proton's resonance frequency range depends on the strength of the applied field. The spectrum above was generated on an instrument with an applied field of approximately 7.1 Tesla, at which strength protons resonate in the neighborhood of 300 million Hz (chemists refer to this as a 300 MHz instrument). If our colleague in another lab takes the NMR spectrum of the same molecule using an instrument with a 2.4 Tesla magnet, the protons will resonate at around 100 million Hz (so we’d call this a 100 MHz instrument). It would be inconvenient and confusing to always have to convert NMR data according to the field strength of the instrument used. Therefore, chemists report resonance frequencies not as absolute values in Hz, but rather as values relative to a common standard, generally the signal generated by the protons in TMS. This is where the ppm – parts per million – term comes in. Regardless of the magnetic field strength of the instrument being used, the resonance frequency of the 12 equivalent protons in TMS is defined as a zero point. The resonance frequencies of protons in the sample molecule are then reported in terms of how much higher they are, in ppm, relative to the TMS signal (almost all protons in organic molecules have a higher resonance frequency than those in TMS, for reasons we shall explore quite soon).
The two proton groups in our methyl acetate sample are recorded as resonating at frequencies 2.05 and 3.67 ppm higher than TMS. One-millionth (1.0 ppm) of 300 MHz is 300 Hz. Thus 2.05 ppm, on this instrument, corresponds to 615 Hz, and 3.67 ppm corresponds to 1101 Hz. If the TMS protons observed by our 7.1 Tesla instrument resonate at exactly 300,000,000 Hz, this means that the protons in our ethyl acetate samples are resonating at 300,000,615 and 300,001,101 Hz, respectively. Likewise, if the TMS protons in our colleague's 2.4 Tesla instrument resonate at exactly 100 MHz, the methyl acetate protons in her sample resonate at 100,000,205 and 100,000,367 Hz (on the 100 MHz instrument, 1.0 ppm corresponds to 100 Hz). The absolute frequency values in each case are not very useful – they will vary according to the instrument used – but the difference in resonance frequency from the TMS standard, expressed in parts per million, should be the same regardless of the instrument.
Expressed this way, the resonance frequency for a given proton in a molecule is called its chemical shift. A frequently used symbolic designation for chemical shift in ppm is the lower-case Greek letter delta (δ). Most protons in organic compounds have chemical shift values between 0 and 12 ppm from TMS, although values below zero and above 12 are occasionally observed. By convention, the left-hand side of an NMR spectrum (higher chemical shift) is called downfield, and the right-hand direction is called upfield.
In our methyl acetate example we included for illustrative purposes a small amount of TMS standard directly in the sample, as was the common procedure for determining the zero point with older NMR instruments.That practice is generally no longer necessary, as modern NMR instruments are designed to use the deuterium signal from the solvent as a standard reference point, then to extrapolate the 0 ppm baseline that corresponds to the TMS proton signal (in an applied field of 7.1 Tesla, the deuterium atom in CDCl3 resonates at 32 MHz, compared to 300 MHz for the protons in TMS). In the remaining NMR spectra that we will see in this text we will not see an actual TMS signal, but we can always assume that the 0 ppm point corresponds to where the TMS protons would resonate if they were present.



|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|