


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 19-9-2020
Date: 26-1-2020
Date: 21-8-2016
|
Chiral acids, such as (+)-tartaric acid, (-)-malic acid, (-)-mandelic acid, and (+)-camphor- 10-sulfonic acid, are used for the resolution of a racemic base.
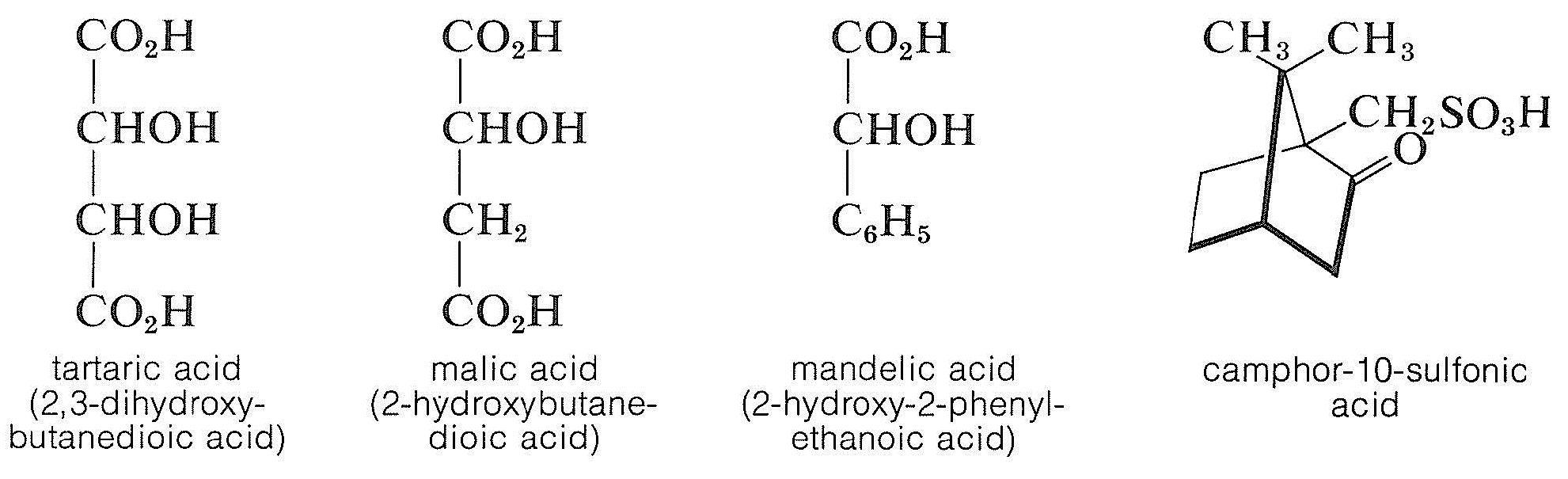
The principle is the same as for the resolution of a racemic acid with a chiral base, and the choice of acid will depend both on the ease of separation of the diastereomeric salts and, of course, on the availability of the acid for the scale of the resolution involved. Resolution methods of this kind can be tedious, because numerous recrystallizations in different solvents may be necessary to progressively enrich the crystals in the less-soluble diastereomer. To determine when the resolution is complete, the mixture of diastereomers is recrystallized until there is no further change in the measured optical rotation of the crystals. At this stage it is hoped that the crystalline salt is a pure diastereomer from which one pure enantiomer can be recovered. The optical rotation of this
enantiomer will be a maximum value if it is "optically" pure because any amount of the other enantiomer could only reduce the magnitude of the measured rotation α.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|