


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 10-8-2020
Date: 11-7-2018
Date: 30-10-2020
|
Rutherford’s nuclear model of the atom helped explain why atoms of different elements exhibit different chemical behavior. The identity of an element is defined by its atomic number (Z), the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of the element. The atomic number is therefore different for each element. The known elements are arranged in order of increasing Z in the periodic table (Figure 1.1). The rationale for the peculiar format of the periodic table is explained later. Each element is assigned a unique one-, two-, or three-letter symbol. The names of the elements are listed in the periodic table, along with their symbols, atomic numbers, and atomic masses. The chemistry of each element is determined by its number of protons and electrons. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons.
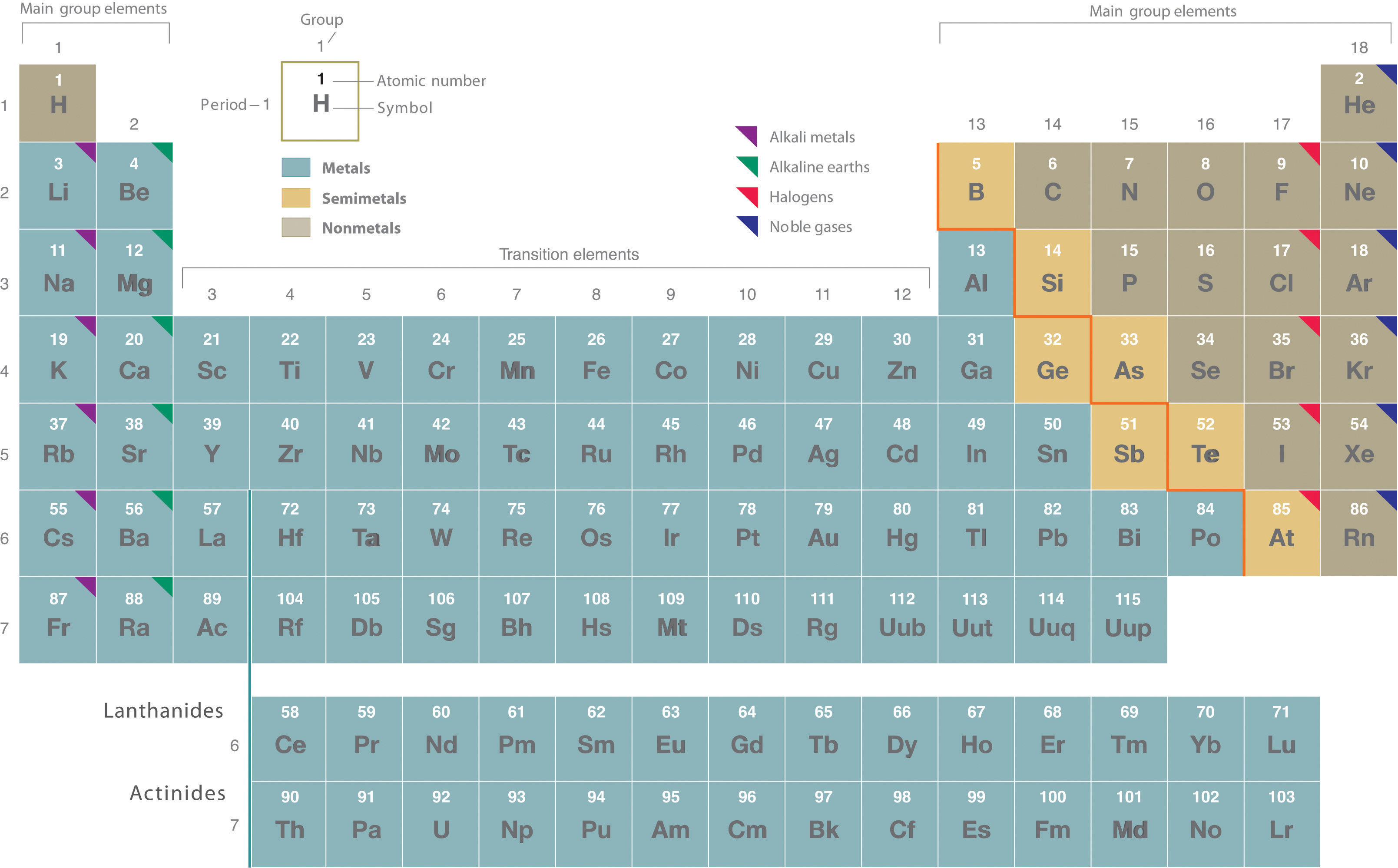
Figure 1.1
: The Periodic Table Showing the Elements in Order of Increasing Z. The metals are on the bottom left in the periodic table, and the nonmetals are at the top right. The semimetals lie along a diagonal line separating the metals and nonmetals.
The elements are arranged in a periodic table, which is probably the single most important learning aid in chemistry. It summarizes huge amounts of information about the elements in a way that facilitates the prediction of many of their properties and chemical reactions. The elements are arranged in seven horizontal rows, in order of increasing atomic number from left to right and top to bottom. The rows are called periods, and they are numbered from 1 to 7. The elements are stacked in such a way that elements with similar chemical properties form vertical columns, called groups, numbered from 1 to 18 (older periodic tables use a system based on roman numerals). Groups 1, 2, and 13–18 are the main group elements, listed as A in older tables. Groups 3–12 are in the middle of the periodic table and are the transition elements, listed as B in older tables. The two rows of 14 elements at the bottom of the periodic table are the lanthanides and the actinides, whose positions in the periodic table are indicated in group 3.



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ضمن أسبوع الإرشاد النفسي.. جامعة العميد تُقيم أنشطةً ثقافية وتطويرية لطلبتها
|
|
|