


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 3-12-2019
Date: 20-7-2018
Date: 3-12-2019
|
Glucose
Carbohydrates have been given non-systematic names, although the suffix ose is generally used. The most common carbohydrate is glucose (C6H12O6). Applying the terms defined above, glucose is a monosaccharide, an aldohexose (note that the function and size classifications are combined in one word) and a reducing sugar. The general structure of glucose and many other aldohexoses was established by simple chemical reactions. The following diagram illustrates the kind of evidence considered, although some of the reagents shown here are different from those used by the original scientists.
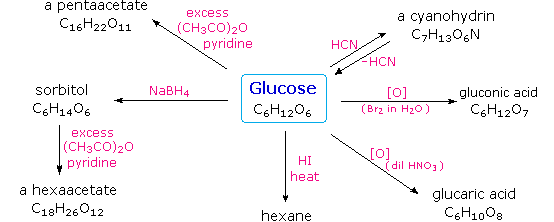
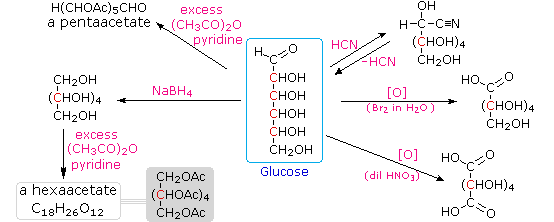
Hot hydriodic acid (HI) was often used to reductively remove oxygen functional groups from a molecule, and in the case of glucose this treatment gave hexane (in low yield). From this it was concluded that the six carbons are in an unbranched chain. The presence of an aldehyde carbonyl group was deduced from cyanohydrin formation, its reduction to the hexa-alcohol sorbitol, also called glucitol, and mild oxidation to the mono-carboxylic acid, glucuronic acid. Somewhat stronger oxidation by dilute nitric acid gave the diacid, glucaric acid, supporting the proposal of a six-carbon chain. The five oxygens remaining in glucose after the aldehyde was accounted for were thought to be in hydroxyl groups, since a penta-acetate derivative could be made. These hydroxyl groups were assigned, one each, to the last five carbon atoms, because geminal hydroxyl groups are normally unstable relative to the carbonyl compound formed by loss of water. It will change to display the suggested products and the gross structure of glucose. The four middle carbon atoms in the glucose chain are centers of chirality and are colored red.
Glucose and other saccharides are extensively cleaved by periodic acid, thanks to the abundance of vicinal diol moieties in their structure. This oxidative cleavage, known as the Malaprade reaction is particularly useful for the analysis of selective O-substituted derivatives of saccharides, since ether functions do not react. The stoichiometry of aldohexose cleavage is shown in the following equation.




|
|
|
|
4 أسباب تجعلك تضيف الزنجبيل إلى طعامك.. تعرف عليها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أكبر محطة للطاقة الكهرومائية في بريطانيا تستعد للانطلاق
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أصواتٌ قرآنية واعدة .. أكثر من 80 برعماً يشارك في المحفل القرآني الرمضاني بالصحن الحيدري الشريف
|
|
|