


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 29-8-2017
Date: 3-9-2017
Date: 13-8-2017
|
Benzene
Benzene (C6H6) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon and by far the most widely used one. Before 1940, the main source of benzene and substituted benzene was coal tar. Currently, it is mainly obtained from catalytic reforming. Other sources are pyrolysis gasolines and coal liquids. Benzene has a unique structure due to the presence of six delocalized π electrons that encompass the six carbon atoms of the hexagonal ring.
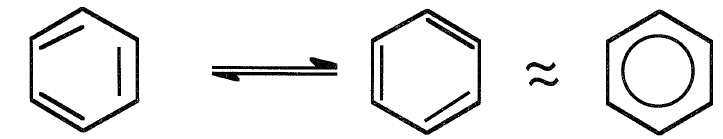
Benzene could be represented by two resonating Kekule structures. It may also be represented as a hexagon with a circle in the middle. The circle is a symbol of the π cloud encircling the benzene ring. The delocalized electrons associated with the benzene ring impart very special
properties to aromatic hydrocarbons. They have chemical properties of single-bond compounds such as paraffin hydrocarbons and doublebond compounds such as olefins, as well as many properties of their own.
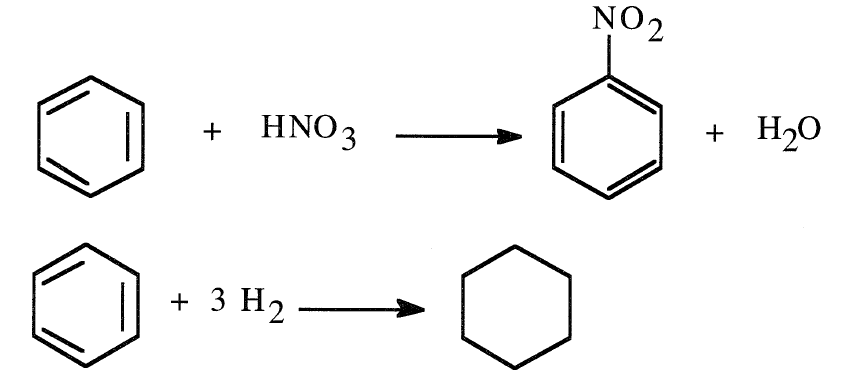
Aromatic hydrocarbons, like paraffin hydrocarbons, react by substitution, but by a different reaction mechanism and under milder conditions. Aromatic compounds react by addition only under severe conditions. For example, electrophilic substitution of benzene using nitric acid produces nitrobenzene under normal conditions, while the addition of hydrogen to benzene occurs in presence of catalyst only under high pressure to give cyclohexane:
Monosubstitution can occur at any one of the six equivalent carbons of the ring. Most of the monosubstituted benzenes have common names such as toluene (methylbenzene), phenol (hydroxybenzene), and aniline (aminobenzene).
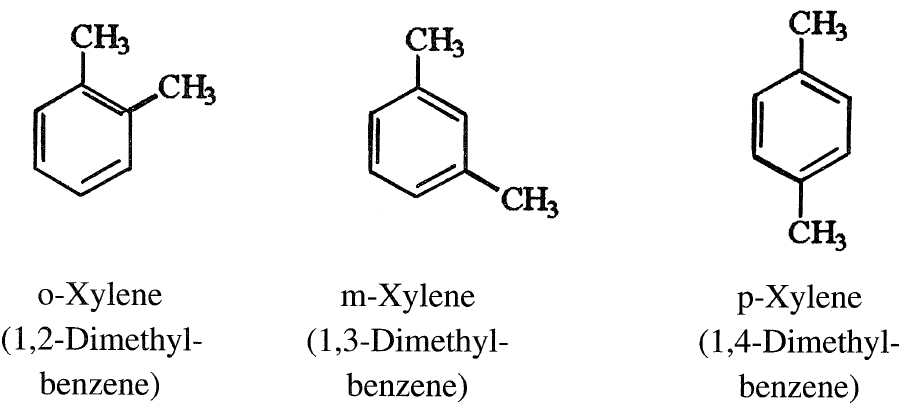
When two hydrogens in the ring are substituted by the same reagent, three isomers are possible. The prefixes ortho, meta, and para are used to indicate the location of the substituents in 1,2-; 1,3-; or 1,4-positions. For example, there are three xylene isomers:
Benzene is an important chemical intermediate and is the precursor for many commercial chemicals and polymers such as phenol, styrene for poly- styrenics, and caprolactom for nylon 6.



|
|
|
|
دور في الحماية من السرطان.. يجب تناول لبن الزبادي يوميا
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العلماء الروس يطورون مسيرة لمراقبة حرائق الغابات
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ضمن أسبوع الإرشاد النفسي.. جامعة العميد تُقيم أنشطةً ثقافية وتطويرية لطلبتها
|
|
|