


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 4-10-2017
Date: 18-1-2016
Date: 8-10-2017
|
THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT
Administration via the gastrointestinal tract involves the drug crossing a number of barriers. A tablet may be dissolved in the mouth or a solution may be swallowed. The drug then enters the stomach via the oesophagus (see Scheme 1). The drug is subjected to digestive enzyme and bacterial changes. The strongly acidic nature of the stomach means that amines may be protonated while carboxylic acids will be in their unionized form. The intestine and colon have a pH that is closer to neutrality and hence there may be more free amine available, while even weak acids may be present as their salts. The pH of the stomach and the intestine varies during the day becoming less acidic after a meal. Hence, the timing of taking medicines can be important. These physico-chemical changes clearly affect the water solubility of drugs and the ease with which they can cross lipid barriers into the blood stream. Once into the circulatory system, a drug will be transported to the liver that is a site of intense metabolic activity.
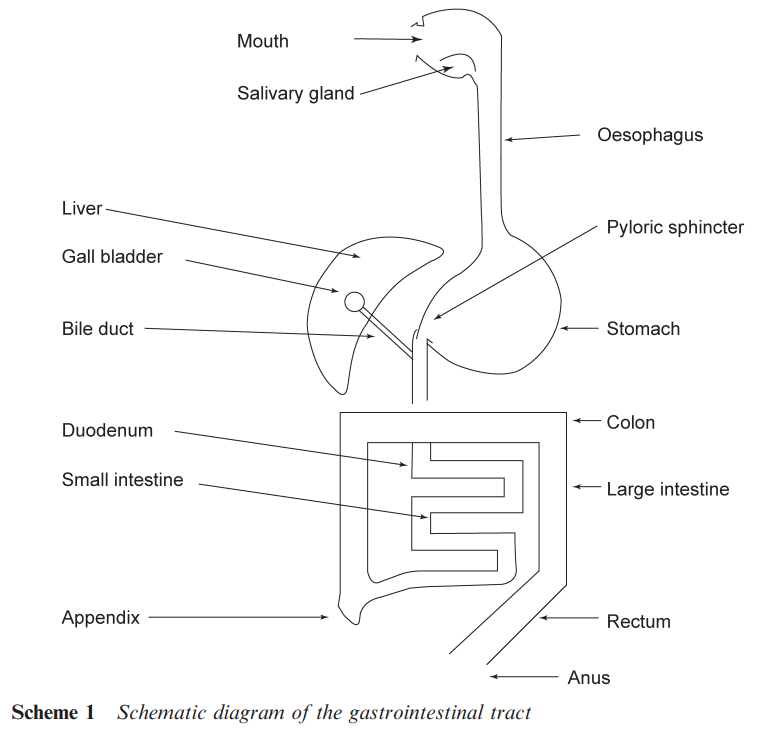
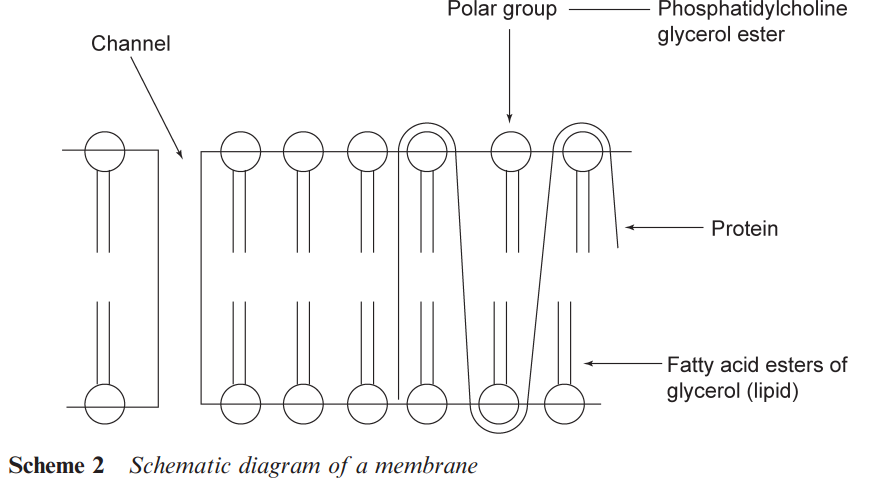
The metabolic changes that affect a drug in the liver may lead to its excretion prior to it reaching the target organ. This loss of material is known as the ‘first pass loss’. As the drug is translocated in the circulatory system, there are additional barriers to cross. A particularly important barrier is the ‘blood brain’ barrier, which prevents some compounds from reaching the brain. Ways of circumventing this barrier are important in developing drugs to treat various diseases of the brain. Structural alterations may also be made to a drug to prevent it reaching the brain and so reduce side effects arising from interactions within the brain. The membranes that a drug may have to cross typically comprise lipid (fatty) bilayers coating a protein through which pass various channels (see Scheme 2).
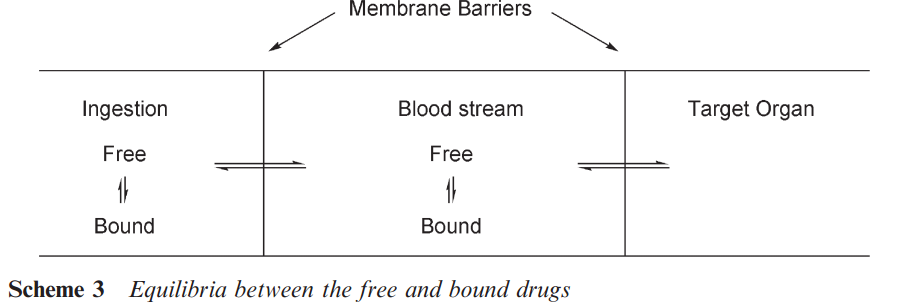
Whether the drug is in the intestine or in the circulatory system, it may not be present as free drug. It may be bound to food particles, to circulatory protein (albumin) or to nucleic acids and platelets. This means that a depot of a bound drug may be formed from which the drug is slowly released. The presence of such a depot may modify and reduce the biologically effective amount of a drug that is available at any one time. It may also prolong its action. Alcohol and some drugs can affect the bio-availability of other drugs by ‘chasing’ them out of the depot leading to a patient experiencing what is in its effect, an overdose. For example, barbiturate sleeping tablets exist substantially in depots. Alcohol can chase barbiturates out of these depots. There have been a number of deaths arising from patients taking sleeping tablets and consuming alcohol at the same time and thus experiencing the consequences of an overdose of the sleeping tablets. Hence the warnings about taking alcohol and medicines. These equilibria can be summarized in Scheme 3.
The combination of these physico-chemical and biological factors leads to the concept of the biological half-life of a drug in the system. However, it should be pointed out that a medicine might have a very different halflife in a healthy adult compared to one suffering from illness.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|