


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2023-10-18
Date: 8-6-2022
Date: 2023-06-07
|
The articulatory variability is reflected acoustically. Figure 6.3 shows the effect of secondary articulations on the acoustics of laterals. This is a spectrogram of a production of [l] whose secondary articulation is shifted from palatalized to velarized. Notice that F2 – associated with frontness and backness – changes, moving from rather high, at around 2100 Hz, to low, at under 1000 Hz.

Figure 6.4 shows a spectrogram of an utterance of the word ‘leaf ’. The lateral portion is marked LAT. At the very end of it, at the point marked 1, there is a spike; this corresponds to the release of the tongue tip from the alveolar ridge and the switch from central to lateral airflow. This change in airflow has an acoustic effect too: notice that the lateral portion is lighter in colour (which means that it is lower in amplitude)
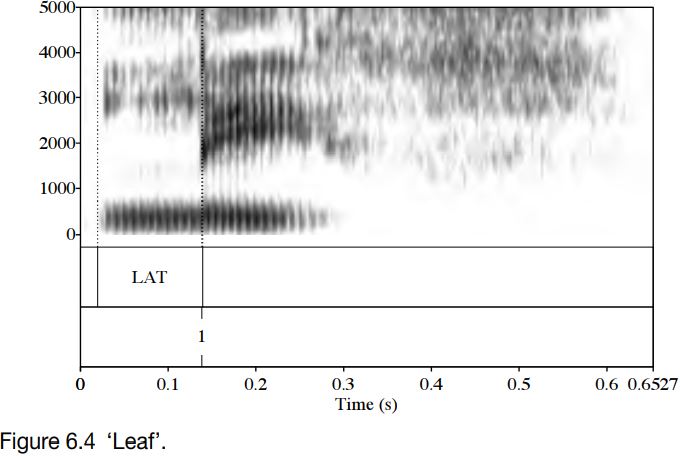
than the following vocalic portion. F2 during the lateral portion is just about visible at around 1600 Hz; this value is consistent with a relatively clear lateral.
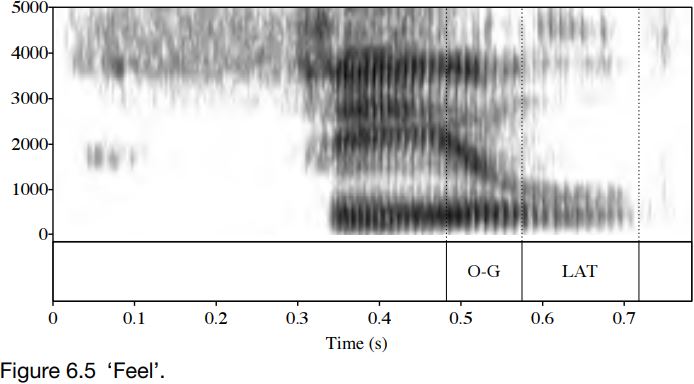
Figure 6.5 is a spectrogram of an utterance of the word ‘feel’. The portion marked O-G (on-glide) shows the formants moving from the values for the vocalic portion – note in particular the high F2 associated with a close front spread vowel – to the values for a velarized lateral. This implies a low F2; and in the portion marked LAT, it can be seen that F2 is at around 1000 Hz. This utterance is by the same speaker as the previous example, so the lateral here is darker than the lateral in ‘leaf ’. The on-glide, it can be noticed, is almost as long as the period of only lateral airflow. Notice that as with ‘leaf ’, lateral airflow induces lower amplitude, seen in the overall lighter spectrogram for the LAT portion.
It should be clear from Figures 6.4 and 6.5 that syllable-initial and syllable-final laterals are far from mirror images of one another. There are two main differences. First, the syllable-initial lateral is clearer, and has a higher F2 than the syllable-final lateral. Secondly, the syllable-initial lateral has a more abrupt ending than the beginning of the syllable-final one: while the transition out of the lateral portion is rapid, in the syllable-final case, the transition into the lateral portion is slow.
|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مكتبة أمّ البنين النسويّة تصدر العدد 212 من مجلّة رياض الزهراء (عليها السلام)
|
|
|