


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 7-1-2022
Date: 13-10-2021
Date: 16-11-2021
|
Biosynthesis of Nonessential amino acids
Nonessential amino acids are synthesized from intermediates of metabolism or, as in the case of tyrosine and cysteine, from the essential amino acids phenylalanine and methionine, respectively. The synthetic reactions for the nonessential amino acids are described below and are summarized in Figure 1. [Note: Some amino acids found in proteins, such as hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine , are produced by posttranslational modification (after incorporation into a protein) of their precursor (parent) amino acids.]
A. Synthesis from α-keto acids
Alanine, aspartate, and glutamate are synthesized by transfer of an amino group to the α-keto acids pyruvate, oxaloacetate, and α-ketoglutarate, respectively. These transamination reactions (Fig. 2) are the most direct of the biosynthetic pathways. Glutamate is unusual in that it can also be synthesized by reversal of oxidative deamination, catalyzed by glutamate dehydrogenase, when ammonia levels are high ).
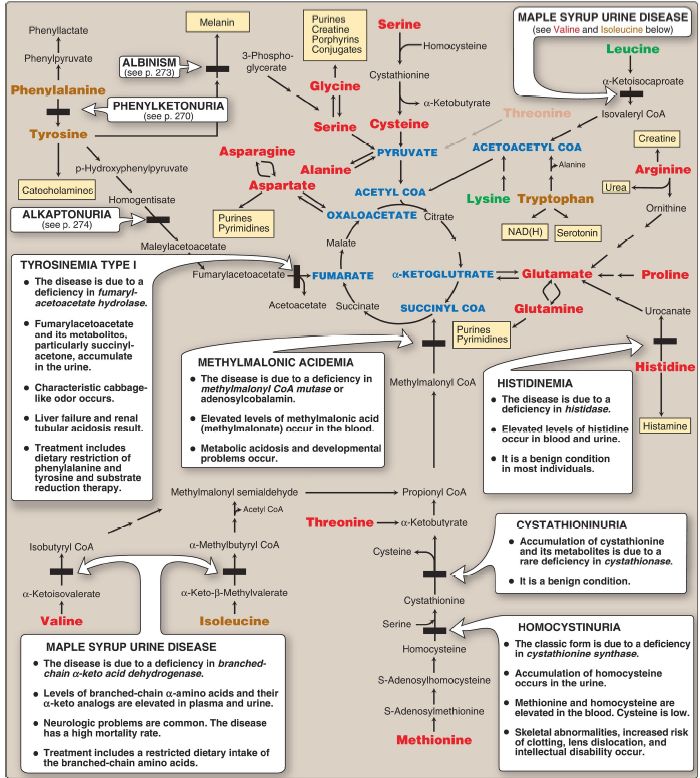
Figure 1:Summary of the metabolism of amino acids in humans. Genetically determined enzyme deficiencies are summarized in white boxes. Nitrogencontaining compounds derived from amino acids are shown in small, yellow boxes. Classification of amino acids is color coded: Red = glucogenic; brown = glucogenic and ketogenic; green = ketogenic. Compounds in BLUE ALL CAPS are the seven metabolites to which all amino acid metabolism converges. CoA = coenzyme A; NAD(H) = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
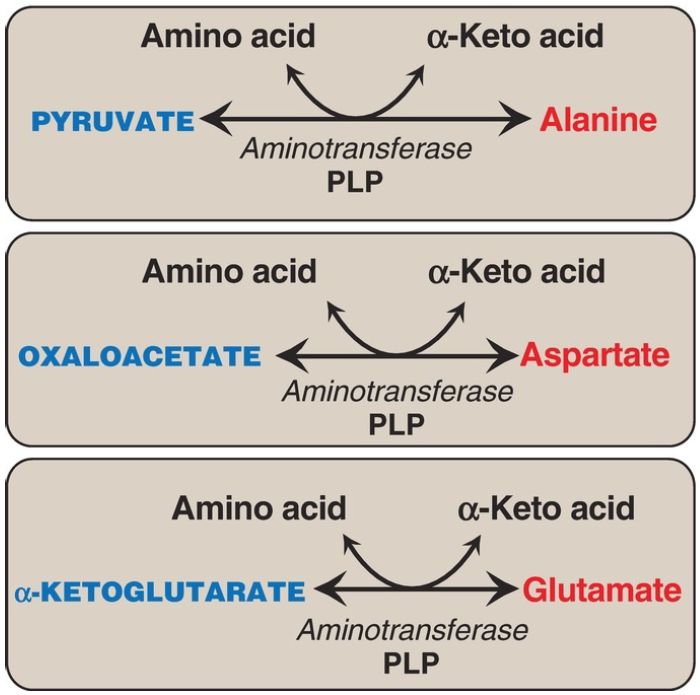
Figure 2: Formation of alanine, aspartate, and glutamate from the corresponding α-keto acids by transamination. PLP = pyridoxal phosphate.
B. Synthesis by amidation
1. Glutamine: This amino acid, which contains an amide linkage with ammonia at the γ-carboxyl, is formed from glutamate by glutamine synthetase . The reaction is driven by the hydrolysis of ATP. In addition to producing glutamine for protein synthesis, the reaction also serves as a major mechanism for the transport of ammonia in a nontoxic form.
2. Asparagine: This amino acid, which contains an amide linkage with ammonia at the β-carboxyl, is formed from aspartate by asparagine synthetase, using glutamine as the amide donor. Like the synthesis of glutamine, the reaction requires ATP and has an equilibrium far in the direction of amide synthesis.
C. Proline
Glutamate via glutamate semialdehyde is converted to proline by cyclization and reduction reactions. [Note: The semialdehyde can also be transaminated to ornithine.]
D. Serine, glycine, and cysteineThe pathways of synthesis for these amino acids are interconnected.
1. Serine: This amino acid arises from 3-phosphoglycerate, a glycolytic intermediate , which is first oxidized to 3-phosphopyruvate and then transaminated to 3-phosphoserine. Serine is formed by hydrolysis of the phosphate ester. Serine can also be formed from glycine through transfer of a hydroxymethyl group by serine hydroxymethyltransferase using N5,N10-MTHF as the one-carbon donor (see Fig. 20.6A). [Note: Selenocysteine (Sec), the 21st genetically encoded amino acid, is synthesized from serine and selenium , while serine is attached to transfer RNA. Sec is found in ~25 human proteins including glutathione peroxidase and thioredoxin reductase .]
2. Glycine: This amino acid is synthesized from serine by removal of a hydroxymethyl group, also by serine hydroxymethyltransferase . THF is the one-carbon acceptor. 3. Cysteine: This amino acid is synthesized by two consecutive reactions in which Hcy combines with serine, forming cystathionine, which, in turn, is hydrolyzed to α-ketobutyrate and cysteine . [Note: Hcy is derived from methionine. Because methionine is an essential amino acid, cysteine synthesis requires adequate dietary intake of methionine.]
E. Tyrosine
Tyrosine is formed from phenylalanine by PAH . The reaction requires molecular oxygen and the coenzyme tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), which is synthesized from guanosine triphosphate. One atom of molecular oxygen becomes the hydroxyl group of tyrosine, and the other atom is reduced to water. During the reaction, BH4 is oxidized to dihydrobiopterin (BH2). BH4 is regenerated from BH2 by NADH-requiring dihydropteridine reductase. Tyrosine, like cysteine, is formed from an essential amino acid and is, therefore, nonessential only in the presence of adequate dietary phenylalanine.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|