


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 28-9-2020
Date: 15-10-2019
Date: 9-10-2020
|
In addition to simple benzene naming and OMP nomenclature, benzene derived compounds are also sometimes used as bases. The concept of a base is similar to the nomenclature of aliphatic and cyclic compounds, where the parent for the organic compound is used as a base (a name for its chemical name. For example, the following compounds have the base names hexane and cyclohexane, respectively.
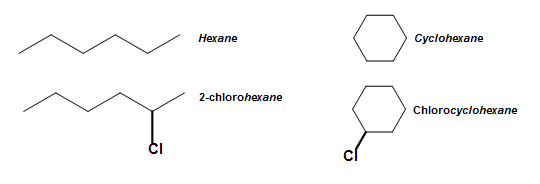
Benzene, similar to these compounds shown above, also has base names from its derived compounds. Phenol (C6H5OH), as introduced previously in this article, for example, serves as a base when other substituents are attached to it. This is best illustrated in the diagram below.
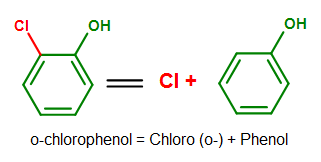
Figure 1. An example showing phenol as a base in its chemical name. Note how benzene no longer serves as a base when an OH group is added to the benzene ring.
Alternatively, we can use the numbering system to indicate this compound. When the numbering system is used, the carbon where the substituent is attached on the base will be given the first priority and named as carbon #1 (C1). The normal priority rules then apply in the nomenclature process (give the rest of the substituents the lowest numbering as you could).
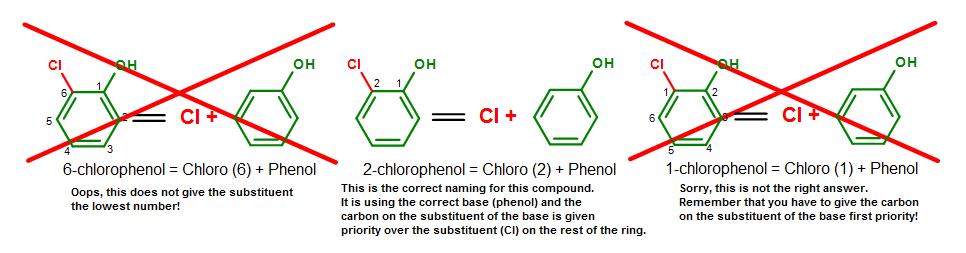
Figure 2. The naming process for 2-chlorophenol (o-chlorophenol). Note that 2-chlorophenol = o-chlorophenol.
Below is a list of commonly seen benzene-derived compounds. Some of these mono-substituted compounds (labeled in red and green), such as phenol or toluene, can be used in place of benzene for the chemical's base name.
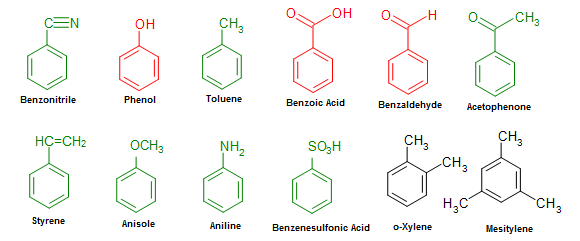
Figure 3. Common benzene derived compounds with various substituents.




|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
سماحة السيد الصافي يؤكد ضرورة تعريف المجتمعات بأهمية مبادئ أهل البيت (عليهم السلام) في إيجاد حلول للمشاكل الاجتماعية
|
|
|