


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 25-6-2020
Date: 5-7-2020
Date: 3-6-2020
|
The terms transition metal (or element) and d block element are sometimes used as if they mean the same thing. They don't - there's a subtle difference between the two terms. We'll explore d block elements first:
You will remember that when you are building the Periodic Table and working out where to put the electrons using the Aufbau Principle, something odd happens after argon. At argon, the 3s and 3p levels are full, but rather than fill up the 3d levels next, the 4s level fills instead to give potassium and then calcium. Only after that do the 3d levels fill. The elements in the Periodic Table which correspond to the d levels filling are called d block elements. The first row of these is shown in the shortened form of the Periodic Table below.
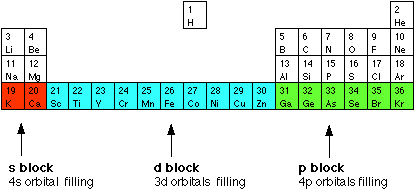
The electronic structures of the d block elements shown are:
| Sc | [Ar] 3d14s2 |
| Ti | [Ar] 3d24s2 |
| V | [Ar] 3d34s2 |
| Cr | [Ar] 3d54s1 |
| Mn | [Ar] 3d54s2 |
| Fe | [Ar] 3d64s2 |
| Co | [Ar] 3d74s2 |
| Ni | [Ar] 3d84s2 |
| Cu | [Ar] 3d104s1 |
| Zn | [Ar] 3d104s2 |
You will notice that the pattern of filling is not entirely tidy! It is broken at both chromium and copper.Transition metals
Not all d block elements count as transition metals!
A transition metal is one which forms one or more stable ions which have incompletely filled d orbitals. On the basis of this definition, scandium and zinc do not count as transition metals - even though they are members of the d block.
By contrast, copper, [Ar] 3d104s1, forms two ions. In the Cu+ ion the electronic structure is [Ar] 3d10. However, the more common Cu2+ ion has the structure [Ar] 3d9. Copper is definitely a transition metal because the Cu2+ ion has an incomplete d level.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|