


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 1-8-2018
Date: 30-6-2019
Date: 1-8-2018
|
Examples of Selective Enolate Alkylation
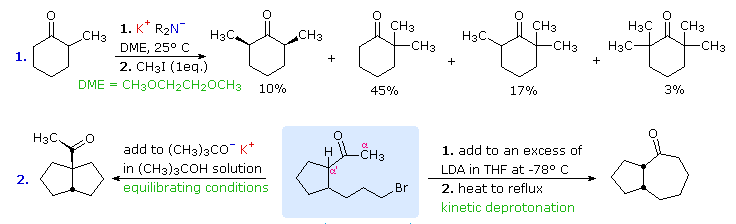
Another aspect of enolate anion alkylation, not yet addressed, is the possibility of electrophilic bonding at oxygen. One example of such behavior will be displayed by clicking the "Toggle Reactions" button. Because of the substantial negative charge on the oxygen of ambident anions, it might be expected that O-alkylation would be the rule rather than the exception. This, in fact, is true when fully or extensively ionized enolate salts are reacted with strong electrophiles. Ionization of enolates is facilitated by high dielectric solvents, such as DMSO and DMF (dimethylformamide), especially for potassium and cesium cation salts. As shown in the lower part of the second diagram, the negatively charged oxygens of DMSO cluster about a cation, providing substantial solvation stabilization. No such solvation exists for the enolate anion, leaving it open to reaction with an electrophile. Lithium enolates have significant covalent character in the metal-oxygen bond, and this retards electrophile attack at oxygen.
Ether solvents such as THF and DME (dimethoxyethane or glyme) are commonly used for alkylations because they are inert to strong base and dissolve enolate salts more effectively than hydrocarbons. The difunctional ether DME (dimethoxyethane) is especially effective at solvating cations; and this fact has led to the preparation of cyclic polyethers, known as crown ethers, which are extraordinarily powerful solvating agents. Crown ethers may be added to enolate salt solutions to enhance their ionization. Indeed, the size of the crown ether can be tailored to fit the cation being used, providing additional control over the course of enolate reactions.
The nomenclature of crown ethers consists of two numbers. The first (larger) number designates the overall ring size. The second number indicates the number of ether oxygens. A symmetrical arrangement of the oxygens in the ring is assumed.



|
|
|
|
5 علامات تحذيرية قد تدل على "مشكل خطير" في الكبد
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
تستخدم لأول مرة... مستشفى الإمام زين العابدين (ع) التابع للعتبة الحسينية يعتمد تقنيات حديثة في تثبيت الكسور المعقدة
|
|
|