


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 17-4-2019
Date: 24-1-2017
Date: 15-2-2019
|
Brönsted-Lowry Definitions
The difficulty of fitting NH3 into a general scheme of acids and bases was solved in 1923 by Johannes Brönsted and Thomas Lowry, who defined an acid as a proton donor and base as a proton acceptor. Thus NH3 acts as a base and accepts a proton (H+) from H2O, and H2O acts as an acid in donating a proton to NH3.
 (1.1)
(1.1)
The reverse reaction is also an acid-base reaction: NH4+ acts as an acid in donating a proton to the base, OH-. In the Brönsted-Lowry scheme, every acid has a conjugate base and every base has a conjugate acid. Thus NH4+ is the acid conjugate to the base NH3, and OH- is the base conjugate to the acid H2O. Similarly, acetic acid, CH3COOH, donates its acidic proton to H2O to produce the conjugate base, acetate ion, CH3CO2-:
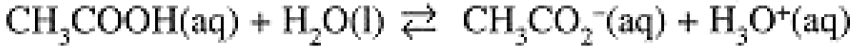 (1.2)
(1.2)
Notice that water can act both as an acid, with conjugate base OH-, and as a base, with conjugate acid H3O+.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|