


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 28-7-2016
Date: 15-1-2017
Date: 3-8-2016
|
Elastic Fibers—Aorta
This figure shows a vertical section through the media of the thoracic aorta. The elastic fibers run in the wavy pattern of corrugated sheets. Between the black-violet elastic fibers are yellow-stained smooth muscle cells. In arteries of the elastic type, elastic structures can be seen as fibers only in vertical sections through the vessel wall. In fact, these structures are elastic membranes or lamellae. The regular staining methods, as used
in histology courses, rarely show elastic fibers. The fibers do not display an organized structural scheme. There is no cross-striation.
Stain: van Gieson resorcin-fuchsin-picric acid; magnification: × 200

Elastic Fibers—Aorta
This section from an aorta wall shows elastic fibers, which dominate the picture in the form of undulating or stretched elements (stained deep blue). Smooth muscle cells (stained light blue) are present between elastic fibers. Only a vertical section of this artery close to the heart will display the elastin as more or less wavy fibers. However, parallel sections show that these are in fact elastic membranes. Elastic fibers withstand degradation using trypsin, heat (cooking) or hydrolysis with dilute acid or alkali. How-ever, elastase, a pancreatic enzyme, will hydrolyze elastin. Tunica me dia of the human thoracic aorta.
Semi-thin section; stain: methylene blue-azure II; magnification: × 320

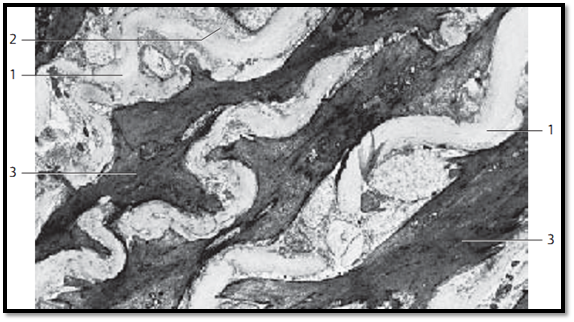
Elastic Fibers—Aorta
Elastic fibers can be easily recognize d in electron microscopic images by their mostly homogeneous central structure with low electron density, called amorphous component or amorphous center. Nevertheless, with appropriate contrasting and higher resolution of a small sector in an edge zone, it is possible to display the fibrils. The fibers show no periodic cross-striation. The small edge zone is called fibrillar component and consists of 15–20 nm thick fibrils. This preparation is from the tunica me dia of the aorta. The snake-like undulating, remarkably light elastic fibers 1 clearly stand out against the smooth muscle cells 3 Elastin, the scleroprotein of elastic fibers, is rich in lysine and alanine. The presence of desmosine and isodesmosine peptides is also characteristic of elastic fibers. Different from collagen, elastin contains little hydroxyproline andno hydroxylysine.
1 Elastic fibers
2 Collagen fibrils
3 Smooth muscle cells
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 4500
References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgart · New York .



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مكتبة أمّ البنين النسويّة تصدر العدد 212 من مجلّة رياض الزهراء (عليها السلام)
|
|
|