
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Liquid-Solid-Liquid
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 9
30-8-2016
1618
Liquid-Solid-Liquid
A small amount of water of mass m = 50 g in a container at temperature T = 273 K is placed inside a vacuum chamber which is evacuated rapidly. As a result, part of the water freezes and becomes ice and the rest becomes vapor.
a) What amount of water initially transforms into ice? The latent heat of fusion (ice/water) qi = 80 cal/g, and the latent heat of vaporization (water/vapor) qv = 600 cal/g.
b) A piece of heated metal alloy of mass M = 325 g and original volume V = 48 cm3 is placed inside the calorimeter together with the ice obtained as a result of the experiment in (a). The density of metal at T = 273 K is ρ0 = 6.8 g/cm3. The thermal capacity is C = 0.12 cal/g K, and the coefficient of linear expansion α = 1.1 × 10-5 K-1. How much ice will have melted when equilibrium is reached?
SOLUTION
a) Since the evaporation is very rapid, the heat to vaporize can only be obtained from the heat of fusion. Therefore, if mi of water becomes solid and mv vaporizes, we may write
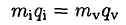 (1)
(1)
Since the total mass m = mi + mv, we have
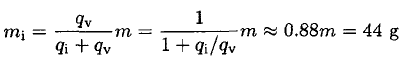 (2)
(2)
If we continue pumping, the ice would, of course, gradually sublimate, but this process takes much longer, so we can neglect it.
b) The metal cools from its initial temperature by transferring heat qm to melt some ice:
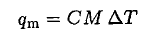 (3)
(3)
where ∆T is the temperature change. This may be determined from the sample’s density before it was placed in the calorimeter. Using the thermal coefficient of volume expansion β, where β = 3α, we have
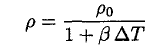 (4)
(4)
The temperature difference ∆T may be found from (4)
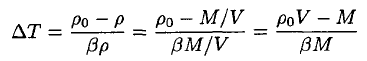 (5)
(5)
Equating the amount of heat required to melt a mass 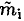 of ice with the heat available in the metal, we have
of ice with the heat available in the metal, we have
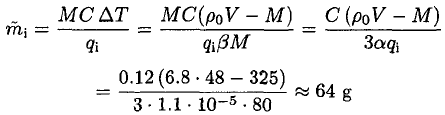 (6)
(6)
This mass exceeds the amount of ice from part (a), so all of it would melt.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















