


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 21-8-2016
Date: 29-8-2016
Date: 30-8-2016
|
Potential of Halved Cylinder
Consider an infinitely long conducting cylinder of radius a with its axis coinciding with the z-axis. One half of the cylinder (cut the long way) (y > 0) is kept at a constant potential V0, while the other half (y < 0) is
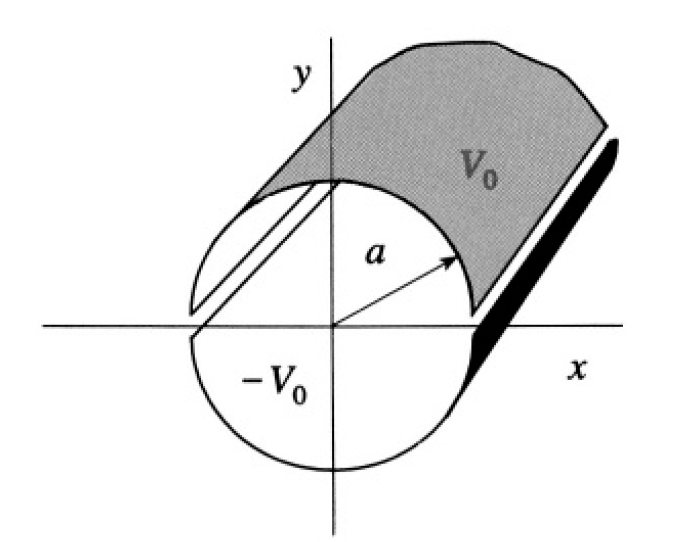
Figure 1.1
kept at a constant potential –V0 (see Figure 1.1). Find the potential for all points inside the cylinder and the field E along the z-axis.
SOLUTION
This problem can be solved by several methods. We will use conformal mapping. Namely, we will try to find a function ω (z), where z = x + iy, to transform the curves of equal potential (in the cross section of the three dimensional body) into parallel straight lines in the u – v plane, where ω = u + iv = f (x, y) +ig (x, y) with both f and g satisfying the Laplace’s equation. We can easily find the solution for the potential problem in the ω plane, and because of the properties of a conformal mapping, the functions u = f (x, y) or v = g (x, y) will be a solution to the initial potential problem. For this problem, we can use the transformation
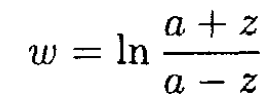 (1)
(1)
This will transform a circle R = a into two straight lines (see Figure 1.2). The upper half of the cylinder will go into v = π/2, and the lower half will
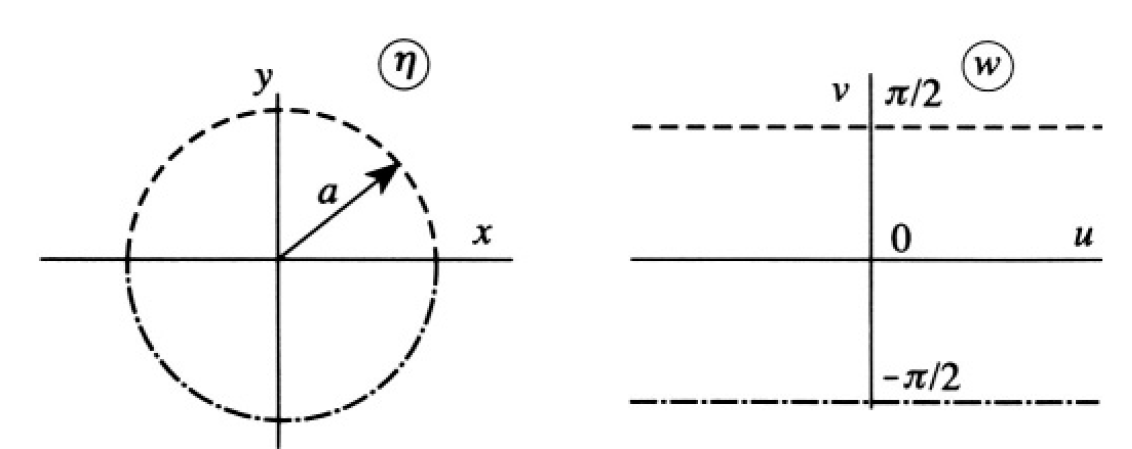
Figure 1.2
go into v = -π/2. So we have
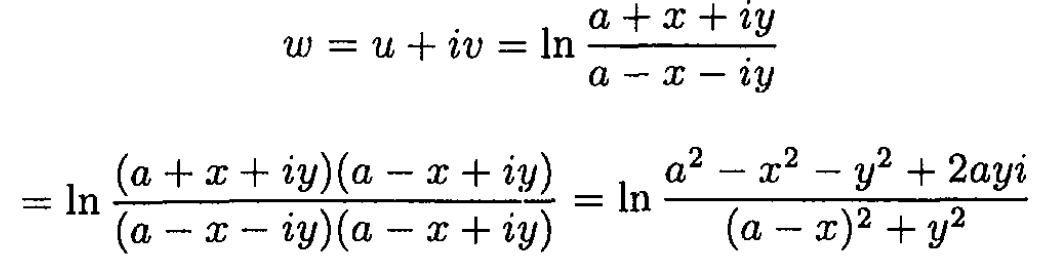 (2)
(2)
Denote the argument of the natural log as ρeiφ where ρ and φ are real. Then.
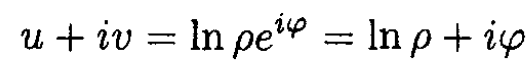
So v = φ. On the other hand,
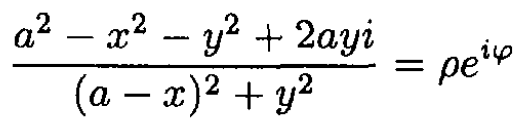 (3)
(3)
For a complex number m + in = ρeiφ, we have
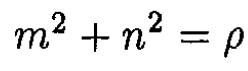 (4)
(4)
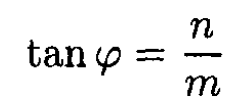 (5)
(5)
Using (5), we obtain from (3)
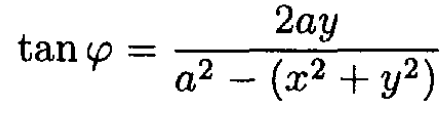
or
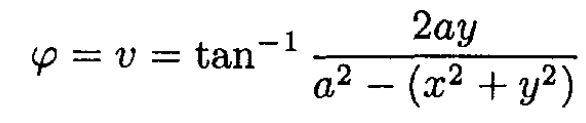
So the potential which satisfies ϕ(v = -π/2) = -V0, ϕ(v = π/2) = V0 is
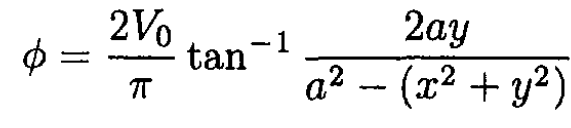 (6)
(6)
On the z-axis
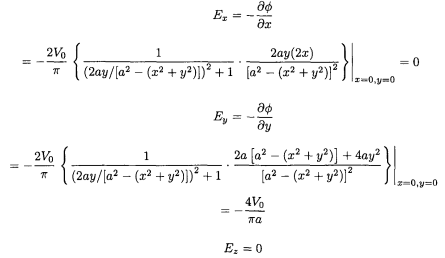
A different solution to this problem may be found in Cronin, Greenberg.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
سماحة السيد الصافي يؤكد ضرورة تعريف المجتمعات بأهمية مبادئ أهل البيت (عليهم السلام) في إيجاد حلول للمشاكل الاجتماعية
|
|
|