


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 3-9-2016
Date: 22-8-2016
Date: 25-7-2016
|
Dumbbell Satellite
Automatic stabilization of the orientation of orbiting satellites utilizes the torque from the Earth’s gravitational pull on a non-spherical satellite in a circular orbit of radius R. Consider a dumbbell-shaped satellite consisting of two point masses of mass m connected by a massless rod of length 2L, much less than R where the rod lies in the plane of the orbit (see Figure 1.1). The orientation of the satellite relative to the direction toward the Earth is measured by angle θ.

Figure 1.1
a) Determine the value of θ for the stable orientation of the satellite.
b) Show that the angular frequency of small-angle oscillations of the satellite about its stable orientation is 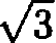 times the orbital angular velocity of the satellite.
times the orbital angular velocity of the satellite.
SOLUTION
Write the Lagrangian in the frame with the origin at the center of the Earth. The potential energy of the satellite is

where M is the mass of the Earth, and R+ and R- are the distances from the center of the Earth to the two masses (see Figure 1.2). Using the formula  (where we
(where we
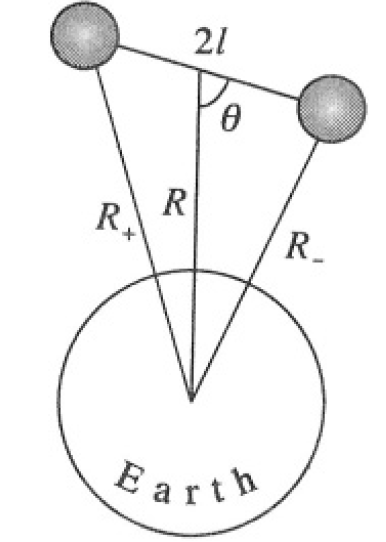
Figure 1.2
disregard the quadratic term (l/R)2), we can rewrite the potential energy in the form
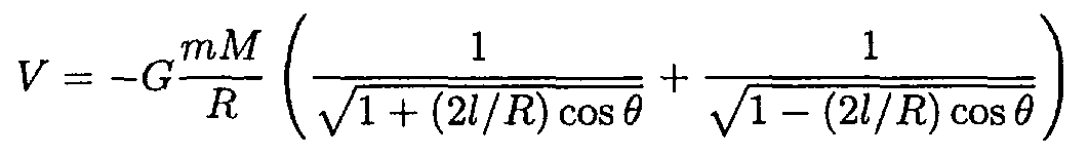 (1)
(1)
Keeping two terms in the expansion of the square root, we obtain
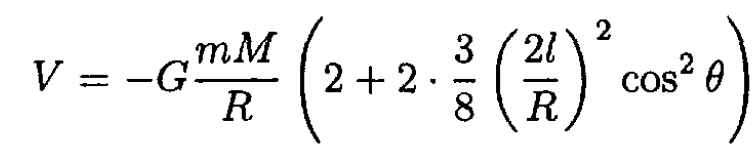 (2)
(2)
We can find the minimum of the potential energy now by solving ∂V/∂θ = 0, which has two solutions:
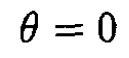
and

For the first solution, ∂2V/∂θ2 > 0, and for the second, ∂2V/∂θ2 < 0. So, at θ = 0, the potential energy has a minimum, and that determines the orientation of the satellite.
b) For small oscillations
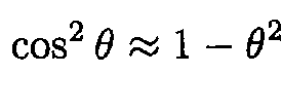
From (2) we obtain
 (3)
(3)
The kinetic energy of the satellite can be written in the same approximation as a sum of its center of mass energy (which is constant) plus the kinetic energy relative to the center of mass:
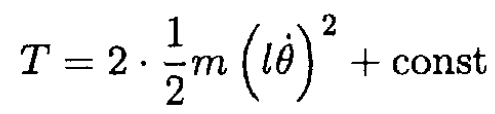
So the Lagrangian is
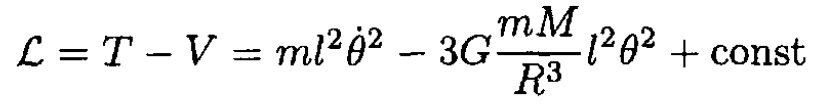
The angular velocity ω0 of the satellite about the Earth may be obtained from the equation for a circular orbit: mω20R = G(mM/R2). From the Lagrangian, we arrive at the angular velocity Ω of small angle oscillations of the satellite, where Ω2 = 3G(M/R3) = 3ω20 and so 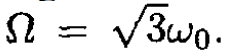 For further details.
For further details.



|
|
|
|
4 أسباب تجعلك تضيف الزنجبيل إلى طعامك.. تعرف عليها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أكبر محطة للطاقة الكهرومائية في بريطانيا تستعد للانطلاق
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تبحث مع العتبة الحسينية المقدسة التنسيق المشترك لإقامة حفل تخرج طلبة الجامعات
|
|
|