
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء والفلسفة

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Relativistic Rocket
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 1 , p 36
13-7-2016
1768
Relativistic Rocket
A rocket having initially a total mass M0 ejects its fuel with constant velocity –u (u> 0) relative to its instantaneous rest frame. According to Newtonian mechanics, its velocity V , relative to the inertial frame in which it was originally at rest, is related to its mass M(V) by the formula
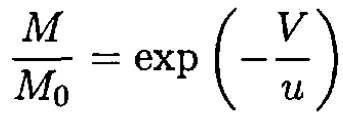
a) Derive this result.
b) Suppose the velocity of the ejecta is limited only by 0 ≤ u ≤ c, and derive the relativistic analogue of the above equation. Show that it reduces to the Newtonian result at the appropriate limit.
SOLUTION
a) Let us consider the short interval dt in the center of mass frame moving with velocity v; the fuel is ejected with velocity u in this frame. At time t' = t + dt the velocity of the rocket increases by dv. The mass M(t) of the rocket decreases by dM(dM < 0) and the mass |dM| of the ejected fuel will have a velocity -u in this frame. Momentum conservation gives
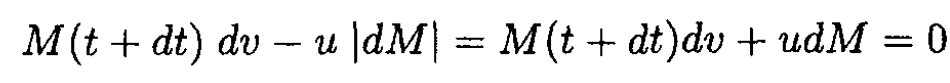 (1)
(1)
where M(t + dt) is the mass of the rocket at time t + dt. Expanding M(t + dt) as
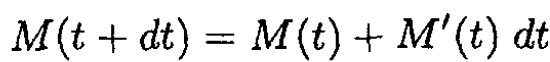
and neglecting second-order terms in the differentials yields
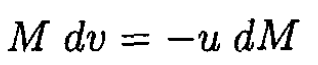 (2)
(2)
Transforming to the lab frame and using dv = dV, where V is the velocity of the rocket in the lab frame, we obtain a solution for the initial condition v(0) = 0:
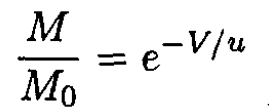 (3)
(3)
b) Write down momentum conservation in the rocket’s frame:
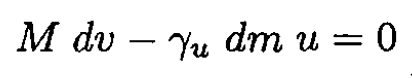 (4)
(4)
where M is the mass of the rocket, dm is the mass of the fuel, and 
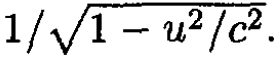 Energy conservation in the frame of the rocket gives
Energy conservation in the frame of the rocket gives
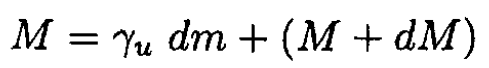 (5)
(5)
We ignored the relativistic corrections to the mass of the rocket in (5) and terms such as 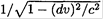 in (4). Substituting from (5) into (4), we have
in (4). Substituting from (5) into (4), we have
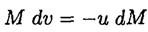 (6)
(6)
which is the same result as obtained in the nonrelativistic calculation of (a). Now we must transform dv from the instantaneous rocket frame to the laboratory frame. Using the equation for the addition of velocities, we have
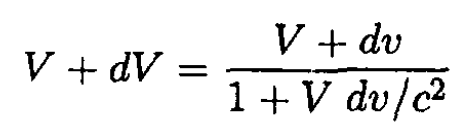 (7)
(7)
where V + dV is the new velocity of the rocket in the lab frame. Rearranging (7) gives
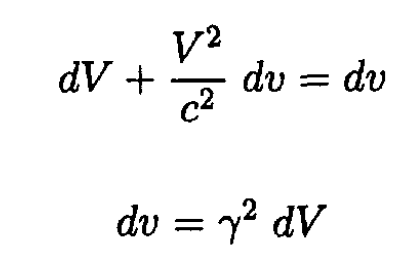 (8)
(8)
where 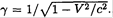 Substituting (8) into (6), we obtain Mγ2 dV = -u dM or
Substituting (8) into (6), we obtain Mγ2 dV = -u dM or
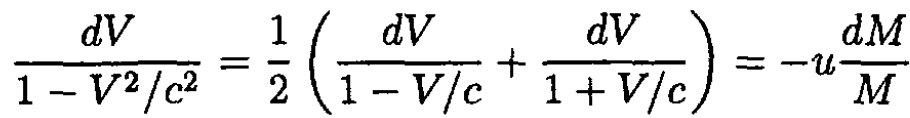 (9)
(9)
Integrating (9), we have
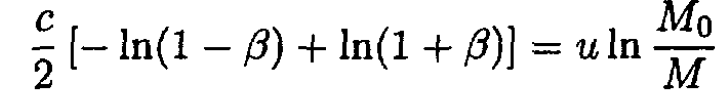 (10)
(10)
where β = V/c, from which we find
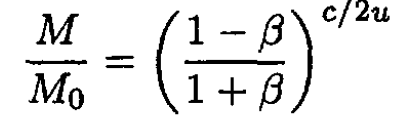 (11)
(11)
If β << 1 then (11) boils down to
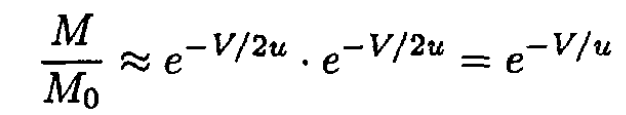
the same result as that obtained in (a).
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















