


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 3-12-2015
Date: 15-3-2021
Date: 30-3-2021
|
Hotspot
DNA sequence analysis can be used to reveal the distribution of mutations within a gene due to spontaneous mutagenesis or following treatment by specific chemicals. Such mutation spectra reveal that neither spontaneous nor induced mutagenesis is random, but mutations cluster in specific regions within a gene. Those DNA sites at which a large number of mutants occur are referred to as “hot spots.” For example, Halliday and Glickman (1) found that 71% of the 729 spontaneous mutants in the lac I gene of E. coli carried mutations in a small region (positions 620–632) with base sequence [5′TGGC3′]3. In contrast, 98% of ICR-191-induced mutations in the lac I gene were +1 and –1 frameshift mutations in runs of repetitive G.C base pairs (2).
There are several possible explanations for genetic hot spots. A trivial one is that there could be a selection bias that favors the detection of mutations at some sites in preference to those at others, but this is probably not true of most observations in the literature. The most likely explanations of most hot spots are unequal distribution of premutational lesions in the gene, differences in processing of lesions in different regions, or some sort of differential DNA repair process. The frameshift mutations produced by N2-(acetylamino)fluorene (AAF, Fig. 1) provide an example in which the reasons for hot spots have been explored in some detail, especially by Fuchs and co-workers (3). This model carcinogen forms adducts on the C8 position of guanine bases. However, the distribution of AAF-induced mutations fails to correspond to the distribution of AAF adducts in DNA. Only 19% of the DNA adducts appear at the sites of mutational hot spots, even though these sites produce 89% of the mutations (4). Subsequent studies have suggested that these hot spots result from differences in processing of DNA damage at particular sites, with premutational events being more readily converted into a mutation at hot spots than at other sites in DNA.
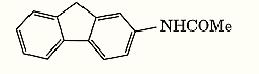
Figure 1. Structure of AAF (2-acetylaminofluorene).
References
1. J. A. Halliday and B. W. Glickman (1991) Mutat. Res. 250, 55–71.
2. M. P. Calos and J. H. Miller (1984) J. Mol. Biol. 153, 39–66.
3. G. R. Hoffmann and R. P. P. Fuchs (1997) Chem. Res. Toxicol. 10, 347–359.
4. R. P. P. Fuchs (1984) J. Mol. Biol. 177, 173–180.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|