


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 29-5-2021
Date: 23-3-2021
Date: 2-6-2021
|
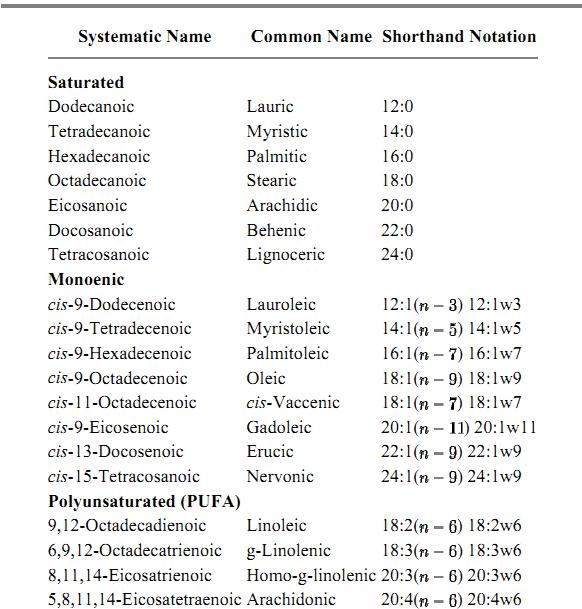
Fatty Acids
The major fatty acids of plants and animals contain even numbers (14 to 26) of aliphatic carbon atoms in straight chains, with a terminal carboxylic acid group. The acids may contain up to six nonconjugated cis-double bonds, generally separated by two single bonds and a single methylene group. Several shorthand nomenclatures are in use to indicate the number of carbon atoms they contain and the number and position of the double bonds; for example, linoleic acid may be written either as 18:2(n - 6 ) or 18:2w6, where the number of carbon atoms in the chain (n = 8 ) is followed by a colon and the number of double bonds (two). The position of the double bonds is set by the number of carbon atoms from the last double bond to the terminal (or w) methyl group (6); in this example, the two double bonds are between carbons 12–13 and 9–10.
Fatty acids appear as the free acids only when bound to serum albumin in blood. They occur in cell membranes primarily as the hydrophobic moiety in phospholipids and other membrane lipids as esters (see Lipids). Linoleic acid is one of a family of essential fatty acids (EFAs) that are required for growth and development in mammals. The EFA all contain the (n - 6 ) terminal structure, which cannot be synthesized by mammalian cells because they are unable to introduce cis-double bonds beyond carbon 9 in fatty acids. The EFA must therefore be obtained from plants whose enzyme systems do synthesize the (n - 6 ) terminal structure. Some of the more abundant fatty acids in cells are listed in Table 1.
Table 1. Some of the More Abundant Fatty Acids in Animals




|
|
|
|
لخفض ضغط الدم.. دراسة تحدد "تمارين مهمة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
طال انتظارها.. ميزة جديدة من "واتساب" تعزز الخصوصية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
بمناسبة مرور 40 يومًا على رحيله الهيأة العليا لإحياء التراث تعقد ندوة ثقافية لاستذكار العلامة المحقق السيد محمد رضا الجلالي
|
|
|