


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 27-12-2015
Date: 7-11-2020
Date: 25-12-2015
|
Alanine (Ala, A (
The amino acid alanine is incorporated into the nascent polypeptide chain during protein biosynthesis in response to four codons—GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG—and represents approximately 8.3% of the residues of the proteins that have been characterized. The alanyl residue incorporated has a mass of 71.09 Da, a van der Waals volume of 67 Å3, and an accessible surface area of 113 Å2. Ala residues are usually relatively variable during divergent evolution, as they are frequently interchanged in homologous proteins with serine, threonine, valine, glutamic acid and proline residues.
The Ala side chain is simply a methyl group:
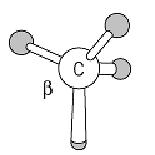
This nonpolar side chain makes Ala residues unreactive chemically, relatively hydrophobic, and not very hydrophilic; consequently, 38% of the Ala residues are fully buried in the folded conformations of proteins. There, the methyl side chain undergoes rapid rotations about the Ca–Cb single bond. Ala has the greatest tendency of all the normal amino acid residues to adopt the alpha-helical conformation in model peptides. It occurs frequently in that conformation in folded protein structures, but at about only half that frequency in beta-sheets and in reverse turns.
References
T. E. Creighton (1993) Proteins: Structures and Molecular Properties, 2nd ed., W. H. Freeman, New York.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|