


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date:
Date: 21-10-2015
Date: 19-10-2015
|
Kingdom
Kingdom is the highest category in the hierarchical classification of organisms created by Carolus Linnaeus around 1750. Linnaeus recognized two kingdoms, plants and animals, a scheme that worked reasonably well for large multicellular organisms but failed as microscopes revealed diverse unicellular organisms. In 1959 Robert Whittaker devised a five-kingdom system that maintained kingdoms Plantae and Animalia but added kingdoms Monera, Protista, and Fungi (see Table).
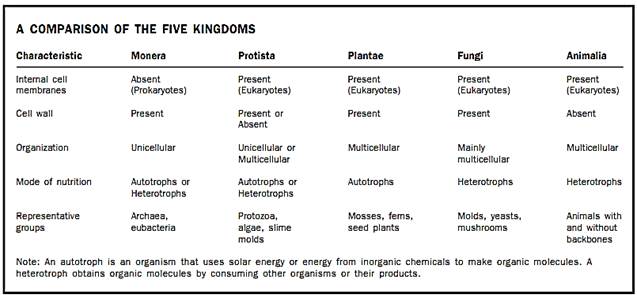
Whittaker placed bacteria in their own kingdom, Monera, because of fundamental organizational differences between prokaryotic bacterial cells, which lack membrane-enclosed nuclei and organelles, and the eukaryotic cells of other organisms that possess internal membranes. Plan- tae, Fungi, and Animalia consist of complex, multicellular eukaryotic organisms that differ from each other in details of cell structure and in how they secure and process energy. Protista is a collection of single-celled eukaryotic organisms and simple multicellular forms, some animal-like, some plantlike.
Molecular evidence, particularly from ribosomal ribonucleic acid (RNA), suggests that the five-kingdom scheme is also too simple. Some biologists believe that Protista should be partitioned into three or more kingdoms. Similarly, kingdom Monera contains two very biochemically distinct groups of prokaryotes: archaebacteria, and eubacteria. A proposed system acknowledges this ancient evolutionary split by creating a higher level of classification, domain, above kingdom. This system distinguishes three domains: Archaea, Eubacteria, and Eukarya (containing protists, plants, fungi, and animals).
References
Margulis, Lynn, and Karlene V. Schwartz. Five Kingdoms: An Illustrated Guide to the Phyla of Life on Earth. New York: W. H. Freeman and Company, 1998.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تستعد لإطلاق الحفل المركزي لتخرج طلبة الجامعات العراقية
|
|
|