


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 12-10-2015
Date: 28-10-2015
Date: 19-10-2015
|
Female Reproductive System
Like the male reproductive system, a primary function of the female reproductive system is to make gametes, the specialized cells that contribute half of the total genetic material of a new person. The female reproductive system has several additional functions: to be the location for joining of the male and female gametes, to protect and nourish the new human during the period of gestation, and to nourish the newborn infant for some time after birth, though lactation and nursing.
Basic Anatomy
The parts of the female reproductive tract normally include two ovaries, two uterine tubes (also called fallopian tubes), a single pear-shaped uterus, and a single vagina. Gamete production is the responsibility of the ovaries, whereas protection and nourishment of the growing embryo and fetus before birth are functions of the uterus. The two uterine tubes, one from each ovary, provide pathways for the female gametes (eggs) to get from the ovaries to the uterus.
The portion of the reproductive tract called the vagina is between the narrow uterine cervix and the outside of the body. In female humans there is a second opening where the urethra from the urinary bladder connects to the outside of the body. The urethral opening is normally separate from, and in front of, the vagina. Both the urethra and the vagina are located between two outer folds of skin called the labia majora and two inner folds, the labia minora. The structure called the clitoris is located where the two folds of the labia minora join each other at the front. The organs of the female reproductive tract are kept in place internally by ligaments that attach the ovaries and uterus to the body wall and by the peritoneal membrane that lines the body cavity containing the intestines and other digestive organs.
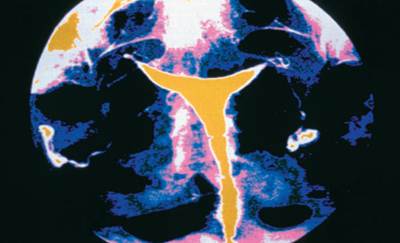
A hysterosalpinograph (X ray) of a normal human uterus and fallopian tubes.
The mammary glands are not part of the female reproductive tract but are important secondary reproductive organs. The mammary glands develop in the tissue underneath the skin but on top of the muscles of the chest. Both males and females start with the same tissues, but normally only females generate the correct hormonal signals to promote development of the mammary glands at puberty. The full ability of mammary glands to synthesize and secrete milk does not occur unless a woman is exposed to the hormonal changes of pregnancy.
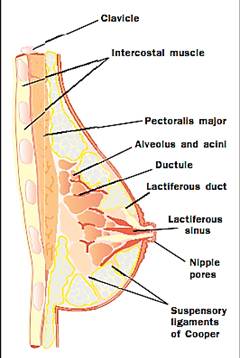
A cross-section of a breast showing the structure of the mammary gland and its placement on the surface muscles of the chest.
The Menstrual Cycle
The primary follicles located in the ovary contain the only cells in the female that can complete the special form of cell division (meiosis) that produces gametes. In females the mature gametes are called egg cells or ova. The production of mature ova is not continuous. Each twenty-eight days or so, one primary follicle (containing one ovum) matures under the influence of hormones from the anterior pituitary, hypothalamus, and the ovary itself. The process of release of a mature ovum from a mature follicle is called ovulation.
While the follicle and ovum are maturing, the follicle secretes hormones that prepare the uterine lining (the endometrium). The endometrium gets thicker and is well supplied with blood vessels. If there are no viable sperm present in the uterine tube as the ovum moves along from the ovary to the uterus, then the ovum will not be fertilized. If fertilization does not occur, or for any other reason a blastocyst (future embryo) fails to implant within the endometrium, the built-up endometrial lining degenerates and is shed. Some bleeding accompanies this process, and the menstrual flow that leaves the woman’s body through her vagina is made of blood and the cells that lined the uterus. Following menstruation, the cycle normally begins again with maturation of a new ovum and buildup of the uterine lining once more.
Women do not have menstrual cycles their entire lives. The first menstrual flow (the menarche) actually means that a female’s first menstrual cycle has just been completed; the first menstrual flow is one commonly used outward sign that a female has entered the transition time called puberty. During puberty, a reproductively immature “girl” becomes a reproductively capable “woman.” With an adequate diet and general good health, puberty typically begins early in a girl’s second decade of life; a first menstrual cycle at eleven or twelve years of age is not unusual. Women also eventually stop having menstrual cycles sometime in their fifth or sixth decade (forty- five to fifty-five years of age). The last menstrual period that a woman experiences is referred to as her menopause. The exact time of menarche and menopause varies significantly from one woman to another.
Hormonal Control of Female Reproduction
Hormones typically coordinate functions in several different organs at the same time. Considerable coordination among the organs of the female reproductive tract is required. Reproduction will not be successful unless ovulation at the ovary occurs near the time when the uterus is prepared to receive the pre-embryo and, soon thereafter, begin forming the placenta. Without a functional placenta the pregnancy will not continue very long after implantation of the blastocyst.
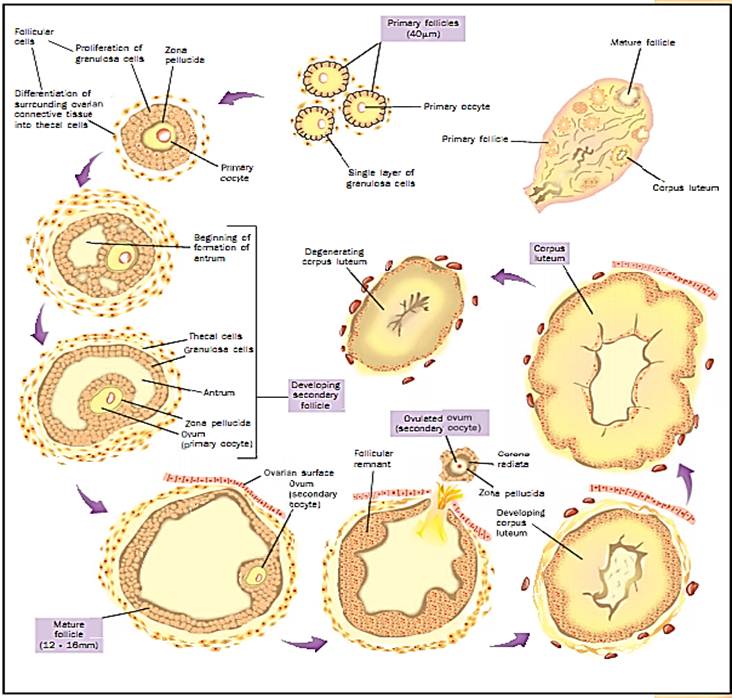
The ovarian cycle
At puberty, the hypothalamus begins its first cyclic release of the peptide hormone gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH), which increases the secretion of peptide hormones called luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary. More FSH and LH are then in the blood flowing through the ovaries. The ovarian cells making up follicles respond to FSH by maturing an ovum. Some of these follicular cells also begin producing their own hormonal signals that prevent other follicles from maturing (the steroids called estrogens) and inhibit the further release of FSH from the anterior pituitary (low levels of estrogens and the peptide hormone inhibin).
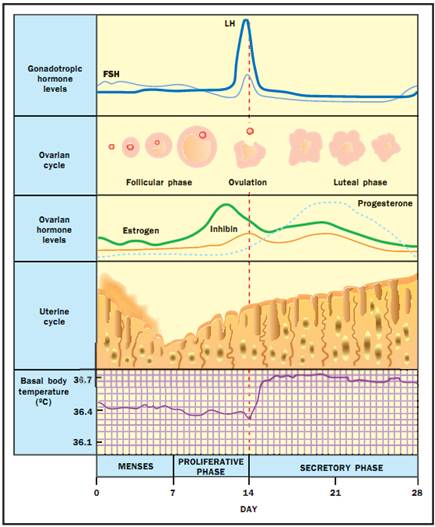
Hormonal profiles throughout the ovarian and uterine cycles with basal body temerature.
About halfway through the cycle on average, fourteen days since the last menstrual flow began, there is a measurable decrease in the woman’s basal body temperature followed by a rapid increase in temperature and in her blood level of LH. This LH surge appears to be the biochemical signal for starting ovulation. Following ovulation, the follicular cells that remain in the ovary become the corpus luteum. The cells of the corpus luteum secrete steroid hormones (progesterone and estrogen). If fertilization and implantation are not successful, the corpus luteum begins to degenerate within ten days of being formed. The decreased levels of progesterone then allow the degeneration and shedding of the endometrium and the next menstrual flow.
Changes Associated with Conception and Pregnancy
In a normal menstrual cycle, only one fertilizable ovum is released. It remains capable of being fertilized for only about twenty-four hours following ovulation, whereas sperm cells may remain capable of fertilizing an ovum for as long as seventy-two hours after they have been deposited into the woman’s reproductive tract by sexual intercourse. Once deposited, the male’s gametes must swim upward through the fluids within the vagina and uterus to arrive at a freshly ovulated ovum in the uterine tube.
A fertilized ovum divides by mitosis, and in about a week produces the blastocyst that implants into the endometrium. If the blastocyst successfully implants in the uterine lining, then a pregnancy occurs. At the start of pregnancy, the corpus luteum continues secreting progesterone under the influence of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) secreted by the implanted embryo. The continuous secretion of progesterone maintains the endometrial lining. As the pregnancy continues, the placenta gradually takes over the reproductive endocrine functions that were performed in the nonpregnant woman by the ovaries. In addition to its endocrine function, the placenta is vitally important in providing nourishment and waste removal for the growing embryo/fetus throughout gestation.
Mammary Glands and Lactation
Newborn infants are not able to feed themselves. The same hormones that are responsible for the changes in the ovaries and uterus during the pregnancy also alter the internal function of the woman’s mammary glands. The synthesis of mother’s milk begins after the delivery of the newborn. An additional peptide hormone called prolactin is secreted from the anterior pituitary. Prolactin helps maintain the secretory capability of the mammary glands for as long as the baby continues to suckle.
References
Boston Women’s Health Collective. Our Bodies Ourselves for the New Century. New York: Simon and Schuster, 1998.
Byer, Curtis O., Louis W. Shainberg, and Grace Galliano. Dimensions of Human Sexuality, 5th ed. Dubuque, IA: McGraw-Hill, 1998.
Mader, Sylvia. Human Reproductive Biology. Dubuque, IA: McGraw-Hill, 1992.
Medscape’s Women's Health MedPulse. <http://womenshealth.medscape.com>.
Saladin, Kenneth S. Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function, 2nd ed. Dubuque, IA: McGraw-Hill, 2001.
Wilcox, Allen J., Clarice R. Weinberg, and Donna D. Baird. “Timing of Sexual Intercourse in Relation to Ovulation.” New England Journal of Medicine 333 (1995): 1517-1521.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
سماحة السيد الصافي يؤكد ضرورة تعريف المجتمعات بأهمية مبادئ أهل البيت (عليهم السلام) في إيجاد حلول للمشاكل الاجتماعية
|
|
|