


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 11-10-2015
Date: 1-11-2015
Date: 19-10-2015
|
Eubacteria
Bacteria are microscopic organisms that comprise the domain Eubacteria. A domain is the highest grouping of organisms, superseding the level of kingdom in the classical Linnaean system of biological classification. There are three domains, two of which, Eubacteria and Archaea, are composed entirely of prokaryotic organisms; the third domain, Eucarya, encompasses all other (eukaryotic) life forms, including the single-cell and multicellular protists, as well as animals, green plants, and fungi. Unlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells lack nuclei and other organelles, and tend to be less complex.
Eubacteria are differentiated from archaea primarily based on chemical composition of cellular constituents. For example, bacterial cell walls are composed of peptidoglycan (though there are examples of bacteria that lack cell walls) while archaeal cell walls are composed of a protein-carbohydrate molecule called pseudopeptidoglycan or other molecules. Bacterial cell membranes are composed of fatty acids joined to glycerol by ester bonds (COOC), while archaeal membranes are composed of isoprenoids rather than glycerol, linked to fatty acids by ether bonds (COC). In addition, the archaea have a more complex ribonucleic acid (RNA) polymerase than bacteria.
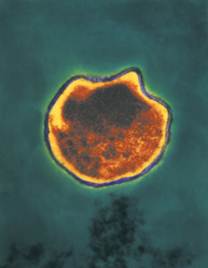
The spherical-shaped Chlamydia pneumonia bacteria
Life Cycle
Reproduction in bacteria involves duplicating the genetic material and dividing the cell into two daughter cells, a process known as binary fission. Under very favorable conditions, certain bacterial cells can divide as often as once every twenty minutes. Some bacteria, such as Clostridium and Bacillus species, possess the ability to form a resting state, or “spore,” when unfavorable conditions are encountered. These spores are very resistant to heat, drying, radiation, and toxic chemicals. Bacterial spores have reportedly been reawakened from a 250-million-year-old salt crystal that existed before the time of the dinosaurs. Sterilization techniques used in medicine must overcome these resistant properties.
Size and Shape
Prokaryotes range in size from 0.2 micrometers to more than 50 micrometers, although the average prokaryote is around 1 to 3 micrometers in size. Eukaryotic cells are approximately one order of magnitude larger, ranging in size from 5 to 20 micrometers in diameter, with an average size of 20 micrometers.
The bacteria come in a number of distinct shapes as well. Common shapes include spherical (coccus), cylindrical (rod), and spiral forms (spirilla). While bacteria are generally regarded as unicellular organisms, there are also examples of bacteria that exist as multicellular colonies, aggregates, or filaments. In addition, bacteria can aggregate on surfaces. Called biofilms, these assemblages can consist of a single species or communities of microorganisms that can participate in metabolic cooperation
Origin of Bacteria
It is not known whether the ancestor of bacteria originated on Earth or elsewhere. Some scientists believe that a life form existed extraterrestrially in the Martian meteorite ALH84001. Whether primitive life originated on Earth or elsewhere, current consensus is that bacteria were present on Earth 3.8 billion years ago.

Colored transmission electron micrograph of the rod-shaped E.coli bacteria, showing its long flagellae.
Diversity
Bacteria show an incredible range of metabolic diversity. Some bacteria can get their energy from light (these are referred to as phototrophic organisms), organic compounds (organotrophic), or inorganic compounds such as hydrogen (H2), sulfur compounds (H2S), inorganic nitrogen compounds or ferrous iron compounds (chemolithotrophic). Some bacteria can make all of their organic compounds by fixing carbon (autotrophic), while others need to break down organic compounds to provide a carbon source (heterotrophic). Many bacteria are capable of fixing atmospheric nitrogen as a nitrogen source, in addition to organic and inorganic sources of nitrogen. Because of this metabolic diversity, bacteria play an important role in biogeochemical cycles such as the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous cycles.
This metabolic diversity also permits them to occupy a wide range of habitats. Bacteria can thrive in extremes of temperature, pH, salt, pressure, or toxic substances. Some bacteria can survive these conditions by spore formation, while other bacteria are able to multiply under extreme conditions. The most primitive bacteria extant today are theromophiles, leading to the consensus view that life arose under extreme conditions. Within and between these extremes, bacteria are found in marine, aquatic, terrestrial and subterranean environments. There are bacteria that are obligate aerobes and some that are obligate anaerobes, and many that fall somewhere in between.
In recent years, highly conserved genes such as the gene coding for the small subunit ribosomal RNA have been used as principal taxonomic characters. As bacteria evolve over time the sequence of this molecule changes, allowing taxonomic relationships between bacteria to be discerned.
Many divisions exist within the Bacteria. An example of this diversity is the subdivision aproteobacteria, whose members are more diverse from each other than are plants from animals. More recently, full genome sequencing has revealed that genes can move between cells and even between species. Thus, bacterial genomes are in constant flux driven by gene acquisition from other species as well as evolutionary forces. The known bacterial tree of life is remarkable, but as 99 percent of bacterial life remains uncultured, this tree will undoubtedly expand greatly over time.
Associations
While most bacteria are free living at some point of their life cycles, many bacteria are capable of living in close associations with other organisms, including eukaryotes. Some of these so-called symbiotic associations are so highly evolved as to be obligate, while other associations are facultative, meaning the symbiotic partners can live apart from each other. In some symbioses, the eukaryotic host provides a highly specialized structure within which the bacteria reside, such as the nitrogen-fixing root nodules found on leguminous plants, such as clover, or the rumen possessed by some herbivorous mammals. Looser symbiotic associations exist where the host provides no specialized structure for the symbiotic bacteria. Organisms that populate the root zone of plants can provide growth benefits; these bacteria are in turn making use of plant products exuded though the roots.
There are also bacteria that are very harmful or even fatal to eukaryotic hosts. An example of this is Yersinia pestis, causative agent of the bubonic plague. Not all associations between bacteria and their eukaryotic hosts have such a drastic result. Many bacteria exist in relatively benign associations with their hosts, such as the Escherichia coli bacteria in the human large intestine. Some resident bacteria can become pathogenic under certain circumstances. These opportunistic pathogens can cause serious infection in hosts whose defenses are compromised by age or previous illness.
Some association can be very intimate, occurring on the intracellular level. It is generally accepted that the eukaryotic chloroplasts and mitochondria arose from associations between bacteria and other cells. These organelles are similar in size to bacteria and contain remnants of bacterial genomes.
References
Friedmann, E. I., J. Wierzchos, C. Ascaso, and Michael Winklhofer. “Chains of Magnetite Crystals in the Meteorite ALH84001: Evidence Of Biological Origin.” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, no. 5 (2001): 2176-2181.
Madigan, M. T., J. T. Martinko, and J. Parker. Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 9th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2000.
Perry, J. J., and J. T. Staley. Microbiology: Dynamics and Diversity. Philadelphia, PA: W. B. Saunders, Co., 1997.
Vreeland, R. H., W. D. Rosenzweig, and D. W. Powers. “Isolation of a 250-Million- Year-Old Halotolerant Bacterium from a Primary Salt Crystal.” Nature 407 (2000): 897-900.



|
|
|
|
4 أسباب تجعلك تضيف الزنجبيل إلى طعامك.. تعرف عليها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أكبر محطة للطاقة الكهرومائية في بريطانيا تستعد للانطلاق
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
بحضور أمينها العام.. العتبة العباسية المقدسة تعقد اجتماعها الدوري لمناقشة أداء أقسامها
|
|
|