


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 14-10-2015
Date: 16-10-2015
Date: 21-10-2015
|
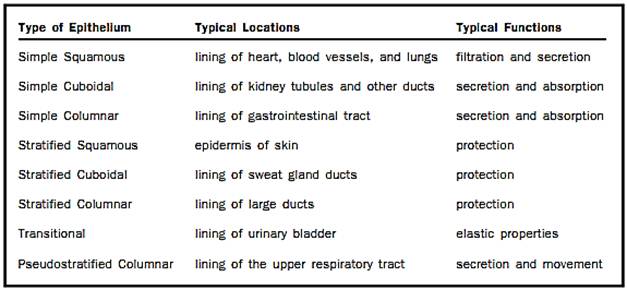
Epithelium
Epithelium is a tissue composed of sheets of cells that are joined together in one or more layers. Epithelia cover the body surface, line body cavities and hollow organs, and form glands. Epithelial tissue forms a barrier between the body and the external environment and plays important roles in protection, filtration, absorption, excretion, and sensation. The rapid regeneration of epithelial cells is important to their protective function. Impervious barriers between cells (tight junctions) allow some epithelia (as in the gut) to tightly regulate flow of materials across them. Glands typically contain clusters of epithelial cells that either secrete their products (such as hormones) into the bloodstream or secrete products (such as digestive enzymes) by way of ducts onto an epithelial surface, such as the epidermis or stomach lining.
Epithelia are classified on the basis of cell shape and number of layers: Squamous cells are thin and flat, cuboidal cells are cubical to round, and columnar cells are tall and cylindrical. A simple epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells, all of which contact a nonliving basement membrane below. A stratified epithelium is composed of two or more cell layers. Each of these classes has four types of epithelium (see table below).
Simple squamous epithelium is a single layer of flat cells, simple cuboidal epithelium has a single layer of cubical cells, and simple columnar epithelium has a single layer of columnar cells. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium is a simple epithelium that looks stratified because some of its cells are shorter than others and do not reach the free surface.
Stratified epithelia are named for the shape of the cells at the surface; the deeper cells may or may not have a different shape. In stratified squamous epithelium, the surface cells are flat; in stratified cuboidal epithelium, the surface cells are cubical or round; and in stratified columnar epithelium, surface columnar cells rest on a basal layer of cuboidal cells. Transitional epithelium, a stratified type found only in the urinary tract, has cells that change shape and move across each other as an organ, such as the bladder, expands and contracts.
References
Gartner, Leslie P., and James L. Hiatt. Color Textbook of Histology. Philadelphia, PA: W. B. Saunders, Co., 1997.
Tortora, Gerard J., and Sandra R. Grabowski. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 9th ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2000.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|