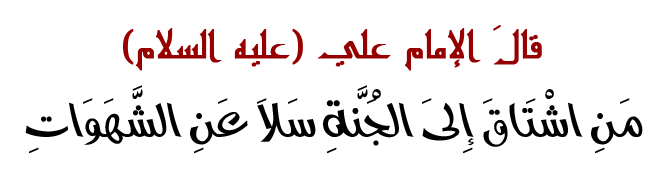
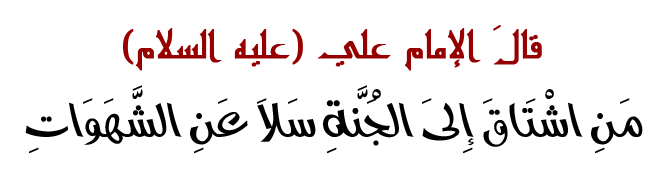

 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 11-5-2021
Date: 21-6-2017
Date: 5-5-2021
|
The bracket polynomial is one-variable knot polynomial related to the Jones polynomial. The bracket polynomial, however, is not a topological invariant, since it is changed by type I Reidemeister moves. However, the polynomial span of the bracket polynomial is a knot invariant, as is a normalized form involving the writhe. The bracket polynomial is occasionally given the grandiose name regular isotopy invariant. It is defined by
 |
(1) |
where  and
and  are the "splitting variables,"
are the "splitting variables,"  runs through all "states" of
runs through all "states" of  obtained by splitting the link,
obtained by splitting the link,  is the product of "splitting labels" corresponding to
is the product of "splitting labels" corresponding to  , and
, and
 |
(2) |
where  is the number of loops in
is the number of loops in  .
.
Letting
 |
 |
 |
(3) |
 |
 |
 |
(4) |
gives a knot polynomial which is invariant under regular isotopy, and normalizing gives the Kauffman polynomial X which is invariant under ambient isotopy as well. The bracket polynomial of the unknot is 1. The bracket polynomial of the mirror image  is the same as for
is the same as for  but with
but with  replaced by
replaced by  .
.
For example, the bracket polynomial of the trefoil knot is given by
 |
(5) |
(Kauffman 1991, p. 35; Livingston 1993, p. 218; Adams 1994, p. 158 gives a form with  replaced by
replaced by  ).
).
The so-called normalized bracket polynomial, also called the Kauffman polynomial X, is defined in terms of the bracket polynomial by
 |
(6) |
where  is the writhe of
is the writhe of  . This normalized version is implemented in the Wolfram Language as KnotData[knot, "BracketPolynomial"].
. This normalized version is implemented in the Wolfram Language as KnotData[knot, "BracketPolynomial"].
REFERENCES:
Adams, C. C. The Knot Book: An Elementary Introduction to the Mathematical Theory of Knots. New York: W. H. Freeman, pp. 148-155 and 157-158, 1994.
Kauffman, L. "New Invariants in the Theory of Knots." Amer. Math. Monthly 95, 195-242, 1988.
Kauffman, L. Knots and Physics. Teaneck, NJ: World Scientific, pp. 25-29, 1991.
Livingston, C. "Kauffman's Bracket Polynomial." Knot Theory. Washington, DC: Math. Assoc. Amer., pp. 217-220, 1993.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|