


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 1-4-2021
Date: 25-4-2021
Date: 13-5-2021
|
Overdrive
Even when a transistor is biased for best operation, a strong input signal can drive it to point B or beyond during part of the cycle. Then, dIC/dIB is reduced, as shown in Fig. 1. Points X and Y in the graph represent the instantaneous current extremes during the signal cycle.
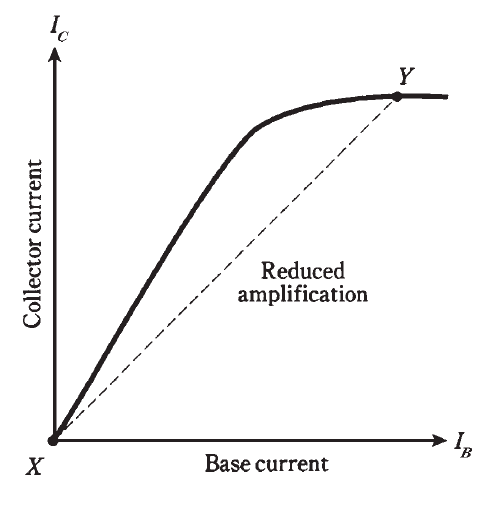
Fig. 1: Excessive input reduces amplification.
When conditions are like those in Fig. 1, there will be distortion in a transistor amplifier. The output waveform will not have the same shape as the input waveform. This nonlinearity can sometimes be tolerated; sometimes it cannot.
The more serious trouble with overdrive is the fact that the transistor is in or near saturation during part of the cycle. When this happens, you’re getting “no bang for the buck.” The transistor is doing futile work for a portion of every wave cycle. This reduces circuit efficiency, causes excessive collector current, and can overheat the base-collector (B-C) junction. Sometimes overdrive can actually destroy a transistor.



|
|
|
|
4 أسباب تجعلك تضيف الزنجبيل إلى طعامك.. تعرف عليها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أكبر محطة للطاقة الكهرومائية في بريطانيا تستعد للانطلاق
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تبحث مع العتبة الحسينية المقدسة التنسيق المشترك لإقامة حفل تخرج طلبة الجامعات
|
|
|