


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 5-6-2021
Date: 30-11-2015
Date: 5-5-2021
|
Recombination Generates Extensive Diversity
KEY CONCEPTS
- The human IgH locus can generate in excess of 104 VH DJH sequences.
- Imprecision of joining and insertion of unencoded nucleotides further increase VH DJH diversity to 108 sequences.
- A recombined VH DJH -CH chain can be paired with in excess of 104 different recombined VK JK -CK or Vλ Jλ -Cλ chains.
A census of the available V, D, J, and C gene segments provides a measure of the diversity that can be accommodated by the variety of the coding regions carried in the germline. In both the IgH and L chain loci, many V gene segments are linked to a much smaller number of C gene segments.
The human λ locus (chromosome 22) has seven Cλ genes, each preceded by its own J segment (FIGURE 16.10). The mouse λ locus (chromosome 16) is much less diverse. The main difference is that in a mouse there are only two V gene segments, each of which is linked to two Jλ Cλ regions. One of the C segments is a pseudogene (nonfunctional gene). This configuration suggests that the mouse suffered in its evolutionary history a large deletion of most of its germline Vλ gene segments.

FIGURE 1. The lambda family consists of Vλ gene segments and a small number of Jλ -Cλ gene segments.
Both the human κ locus (chromosome 2) and the mouse κ locus (chromosome 6) have only one C gene segment, preceded by six J gene segments (one of them being a pseudogene) (FIGURE
2). The Vκ gene segments occupy a large cluster on the chromosome, upstream of the Cκ region. The human cluster has two regions. Just upstream of the Cκ gene segment a 600-kb region contains the Jκ segments and 40 Vκ gene segments. A gap of 800 kb separates this region from another cluster of 36 V gene segments.
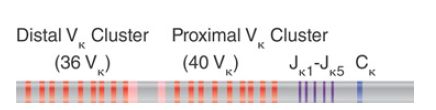
FIGURE 2. The human and mouse Igκ families consist of VK gene segments and five functional JK segments linked to a single CK gene segment. VK genes include nonfunctional pseudogenes.
The VH , Vκ , and Vλ gene segments are segregated into families. A family comprises members that share more than 80% amino acid identity. In humans, the VH locus comprises six VH families: VH 1 through VH 6. VH 3 and VH 4 are the largest families, each with more than 10 functional members; VH 6 is the smallest family, consisting of one member only. In mice, the Vκ locus comprises about 18 Vκ families, which vary in size from 2 to 100 members. Like other families of related genes, related V gene segments form subclusters, which were generated by duplication and divergence of individual ancestral members. Many of the V segments are pseudogenes. Although nonfunctional, some of these may function as donors of partial V sequences in secondary rearrangements.
A given lymphocyte expresses either a κ or a λ chain to be paired with a VH DJH -CH chain. In humans, about 60% of B cells express κ chains and about 40% express λ. In the mouse, 95% of B cells express a κ chain, presumably because of the reduced number of λ gene segments available.
The single IgH chain locus (human chromosome 14) consists of multiple discrete segments (FIGURE 16.12). The furthest 3′ member of the VH cluster is separated by only 20 kb from the first D segment. The D segments (30) are spread over approximately 50 kb, followed by the cluster of 6 JH segments. Over the next 220 kb lie all the CH genes. In addition to the nine functional CH genes, there are two pseudogenes. The human IgH locus organization suggests that a Cγ gene was duplicated to generate the Cγ-Cγ-Cε- Cα subcluster, after which the entire subcluster was then tandemly duplicated. The mouse IgH locus (chromosome 12) has more VH gene segments, fewer D and J segments, and eight (instead of nine) CH genes.

FIGURE 3. A single gene cluster in humans contains all the information for the IgH chain. Depicted is a schematic map of the human IgH chain locus.
The human IgH locus alone can produce more than 104 different VH DJH sequences by combining 51 VH genes, 30 D segments, and 6 JH segments. This degree of diversity is further compounded by the imprecision in the VH DJH joinings, the insertion of unencoded nucleotide (N) additions, and use of multiple D-D segments. By combining any one of more than 50 V gene segments with any 1 of 5 JK segments the human κ locus has the potential to produce 300 different VK J Ksegments. These, however, are conservative estimates, because more diversity is introduced by insertion of untemplated N nucleotides, albeit at lower frequency than in VH DJH .
Further diversity is produced by pairing of the same VH DJH -C chain with different VK JK -CK or Vλ Jλ -Cλ chains. Finally, diversification in individual genes after VH DJH , VK JK , and Vλ Jλ recombination occurs by somatic hypermutation (SHM) .



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مكتبة أمّ البنين النسويّة تصدر العدد 212 من مجلّة رياض الزهراء (عليها السلام)
|
|
|