


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 10-8-2018
Date: 3-1-2020
Date: 18-2-2020
|
We come now to the question of why nonequivalent protons have different chemical shifts. The chemical shift of a given proton is determined primarily by its immediate electronic environment. Consider the methane molecule (CH4), in which the protons have a chemical shift of 0.23 ppm. The valence electrons around the methyl carbon, when subjected to B0, are induced to circulate and thus generate their own very small magnetic field that opposes B0. This induced field, to a small but significant degree, shields the nearby protons from experiencing the full force of B0, an effect known as local diamagnetic shielding. The methane protons therefore do not experience the full force of B0 - what they experience is called Beff, or the effective field, which is slightly weaker than B0.

Therefore, their resonance frequency is slightly lower than what it would be if they did not have electrons nearby to shield them.
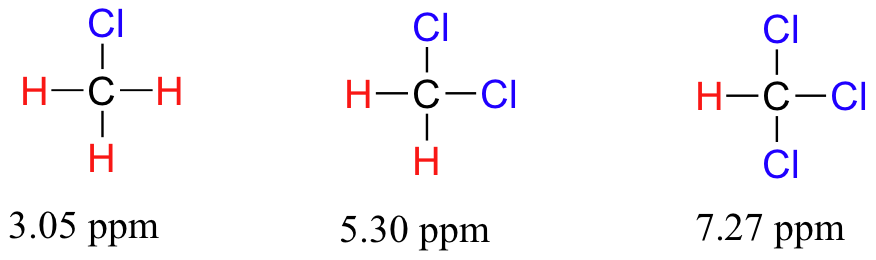
Now consider methyl fluoride, CH3F, in which the protons have a chemical shift of 4.26 ppm, significantly higher than that of methane. This is caused by something called the deshielding effect. Because fluorine is more electronegative than carbon, it pulls valence electrons away from the carbon, effectively decreasing the electron density around each of the protons. For the protons, lower electron density means less diamagnetic shielding, which in turn means a greater overall exposure to B0, a stronger Beff, and a higher resonance frequency. Put another way, the fluorine, by pulling electron density away from the protons, is deshielding them, leaving them more exposed to B0. As the electronegativity of the substituent increases, so does the extent of deshielding, and so does the chemical shift. This is evident when we look at the chemical shifts of methane and three halomethane compounds (remember that electronegativity increases as we move up a column in the periodic table).

To a large extent, then, we can predict trends in chemical shift by considering how much deshielding is taking place near a proton. The chemical shift of trichloromethane is, as expected, higher than that of dichloromethane, which is in turn higher than that of chloromethane.
The deshielding effect of an electronegative substituent diminishes sharply with increasing distance:

The presence of an electronegative oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or sp2-hybridized carbon also tends to shift the NMR signals of nearby protons slightly downfield:

Table 2 lists typical chemical shift values for protons in different chemical environments.
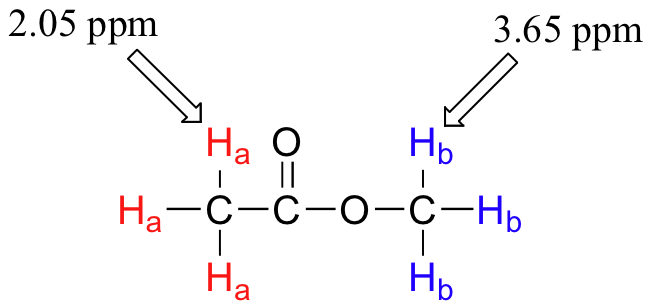
Armed with this information, we can finally assign the two peaks in the the 1H-NMR spectrum of methyl acetate that we saw a few pages back. The signal at 3.65 ppm corresponds to the methyl ester protons (Hb), which are deshielded by the adjacent oxygen atom. The upfield signal at 2.05 ppm corresponds to the acetate protons (Ha), which is deshielded - but to a lesser extent - by the adjacent carbonyl group.
Finally, a note on the use of TMS as a standard in NMR spectroscopy: one of the main reasons why the TMS proton signal was chosen as a zero-point is that the TMS protons are highly shielded: silicon is slightly less electronegative than carbon, and therefore donates some additional shielding electron density. Very few organic molecules contain protons with chemical shifts that are negative relative to TMS.




|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة الحسينية تطلق فعاليات المخيم القرآني الثالث في جامعة البصرة
|
|
|