
 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 18-1-2020
Date: 21-9-2020
Date: 18-9-2018
|
The "optical purity" is a comparison of the optical rotation of a pure sample of unknown stereochemistry versus the optical rotation of a sample of pure enantiomer. It is expressed as a percentage. If the sample only rotates plane-polarized light half as much as expected, the optical purity is 50%.

Because R and S enantiomers have equal but opposite optical activity, it naturally follows that a 50:50 racemic mixture of two enantiomers will have no observable optical activity. If we know the specific rotation for a chiral molecule, however, we can easily calculate the ratio of enantiomers present in a mixture of two enantiomers, based on its measured optical activity. When a mixture contains more of one enantiomer than the other, chemists often use the concept of enantiomeric excess (ee) to quantify the difference. Enantiomeric excess can be expressed as:
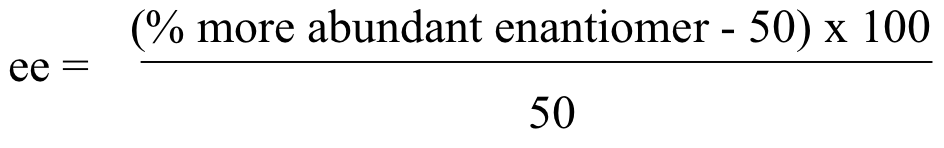
For example, a mixture containing 60% R enantiomer (and 40% S enantiomer) has a 20% enantiomeric excess of R: ((60-50) x 100) / 50 = 20 %.



|
|
|
|
لخفض ضغط الدم.. دراسة تحدد "تمارين مهمة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
طال انتظارها.. ميزة جديدة من "واتساب" تعزز الخصوصية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مشاتل الكفيل تزيّن مجمّع أبي الفضل العبّاس (عليه السلام) بالورد استعدادًا لحفل التخرج المركزي
|
|
|