

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
X-ray fluorescence elemental analysis
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
247
2025-09-02
64
X-ray fluorescence elemental analysis
Key points: Qualitative and quantitative information on the elements present in a compound may be obtained by exciting and analysing X-ray emission spectra. As discussed in Section 8.9, ionization of core electrons can occur when a material is exposed to short-wavelength X-rays. When an electron is ejected in this way, an electron from a higher energy orbital can take its place and the difference in energy is released in the form of a photon, which is also typically in the X-ray region with an energy characteristic of the atoms present. This fluorescent radiation can be analysed either by energy dispersive analysis or by wavelength-dispersive analysis. By matching the peaks in the spectrum with the characteristic values of the elements it is possible to identify the presence of a particular element. This is the basis of the X-ray fluorescence (XRF) technique. The intensity of the characteristic radiation is also directly related to the amount of each element in the material. Once the instrument is calibrated with appropriate standards it can be used to determine quantitatively most elements with Z > 8 (oxygen). Figure 8.41 shows a typical XRF energy-dispersive spectrum. A technique similar to XRF is used in electron microscopes where the method is known as energy-dispersive analysis of X-rays (EDAX) or energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). Here the X-rays generated by bombardment of a sample by energetic electrons result in the ejection of core electrons and X-ray emission occurs as the outer electrons fall into the vacancies in the core levels. These X-rays are characteristic of the elements present and their intensities are representative of the amounts present. The spectrum can be analysed to determine qualitatively and quantitatively the presence and amount of most elements (generally those with Z > 8) in the material.
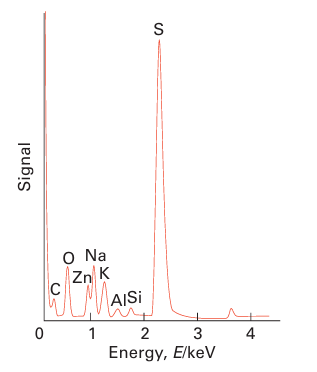
Figure 8.41 An XRF spectrum obtained from a metal silicate sample showing the presence of various elements by their characteristic X-ray emission lines.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















