


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 2-1-2018
Date: 20-12-2018
Date: 25-11-2018
|
Metal borides
Solid state metal borides are characteristically extremely hard, involatile, high melting and chemically inert materials which are industrially important with uses as refractory materials and in rocket cones and turbine blades, i.e. components that must withstand extreme stress, shock and high temperatures. Preparative routes to metal borides are varied, as are their structures. Some may be made by direct combination of the elements at high temperatures, and others from metal oxides.
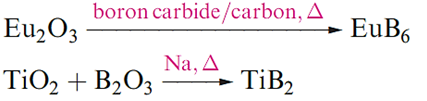
Metal borides may be boron- or metal-rich, and general families include MB3, MB4, MB6 , MB10, MB12, M2B5 and M3B4 (B-rich), and M3B, M4B, M5B, M3B2 and M7B3 (Mrich).
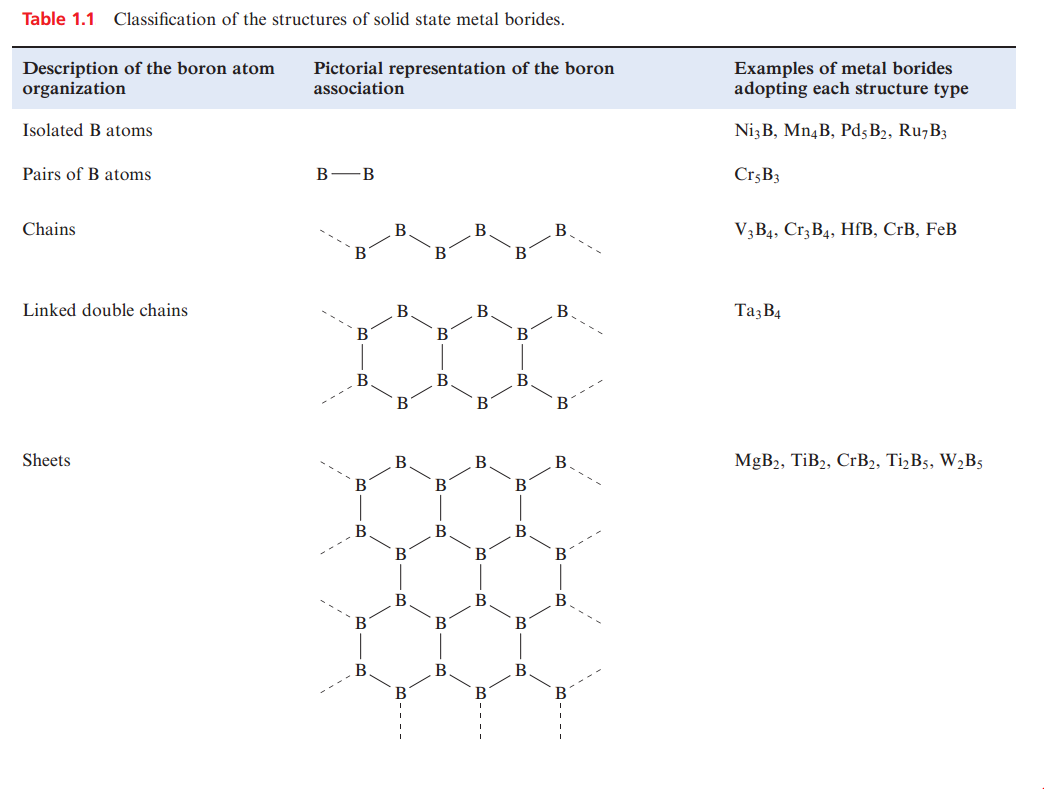
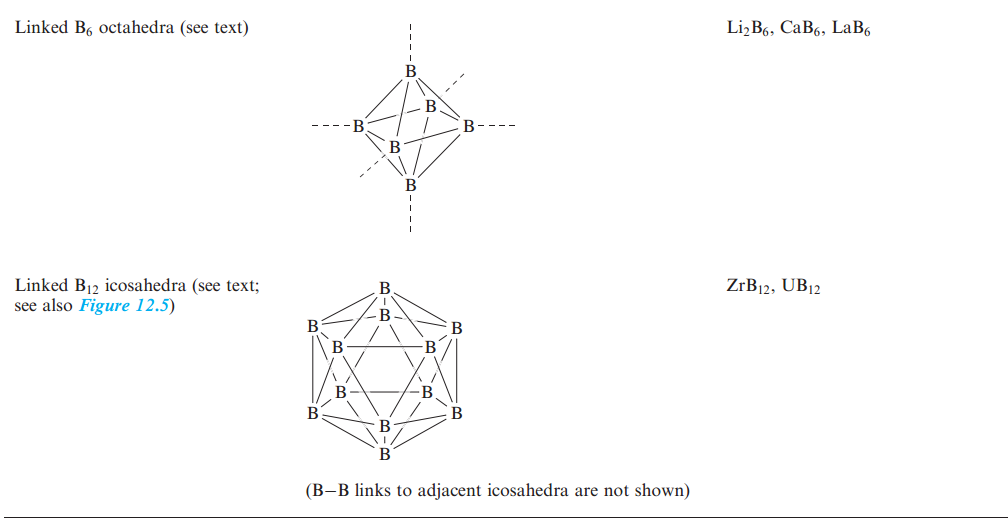
The formulae bear no relation to those expected on the basis of the formal oxidation states of boron and metal. The structural diversity of these materials is so great as to preclude a full discussion here, but we can conveniently consider them in terms of the categories shown in Table 1.1, which are identified in terms of the arrangement of the B atoms within a host metal lattice. The structure type of the MB6 borides (e.g. CaB6) can be envisaged by likening it to that of a CsCl lattice with B6-units (Table 1.1) replacing Cl- ions. However, the B_B distances between adjacent B6-octahedra are similar to those within each unit and so a ‘discrete ion’ model is not actually appropriate.
The structure type of MB12 (e.g. UB12) can similarly be described in terms of an NaCl lattice in which the Cl- ions are replaced by B12-icosahedra (Table 1.1). Although this summary of metal borides is brief, it illustrates the complexity of structures frequently encountered in the chemistry of boron. Research interest in metal borides has been stimulated since 2001 by the discovery that MgB2 is a superconductor with a critical temperature, Tc, of 39K.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|