


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 11-8-2017
Date: 25-7-2017
Date: 9-5-2016
|
ALKYLATION OF BENZENE
Benzene can be alkylated in the presence of a Lewis or a Bronsted acid catalyst. Olefins such as ethylene, propylene, and Cl2–Cl4 alpha olefins are used to produce benzene alkylates, which have great commercial value. Alkyl halides such as monochloroparaffins in the Cl2–Cl4 range also serve this purpose.
The first step in alkylation is the generation of a carbocation (carbonium ion). When an olefin is the alkylating agent, a carbocation intermediate forms.
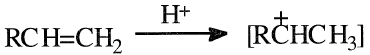
Carboncations also form from an alkyl halide when a Lewis acid catalyst is used. Aluminum chloride is the commonly used Friedel-Crafts alkylation catalyst. Friedel-Crafts alkylation reactions have been reviewed by Roberts and Khalaf:
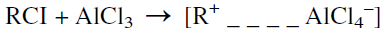
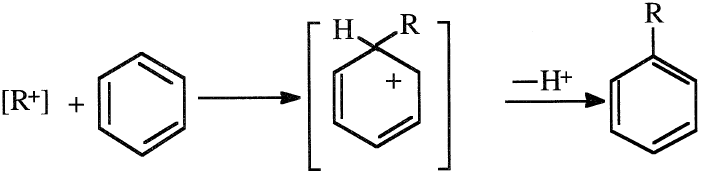
The next step is an attack by the carbocation on the benzene ring, followed by the elimination of a proton and the formation of a benzene alkylate:
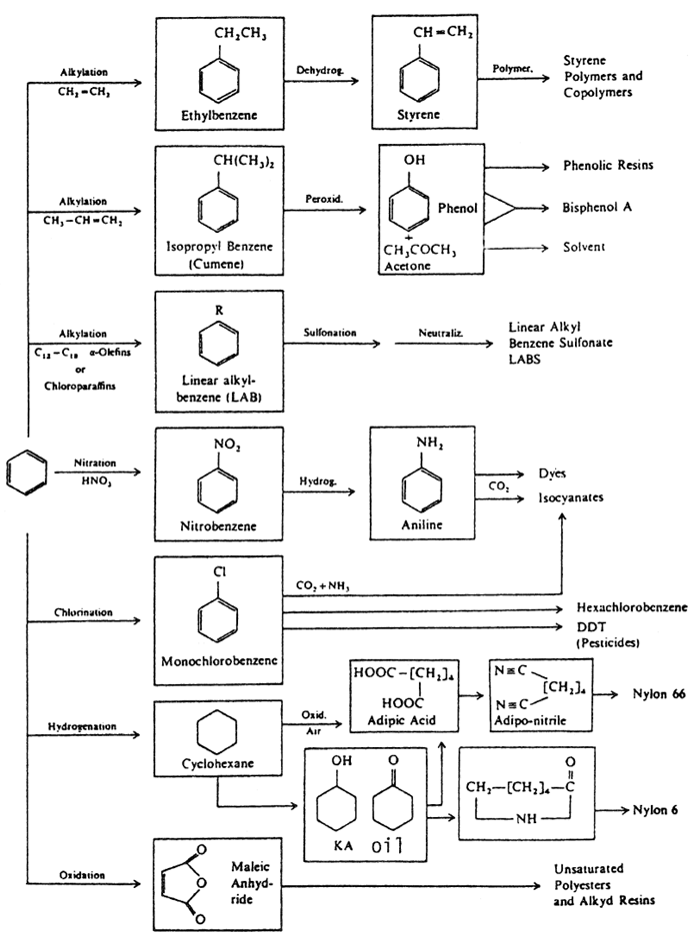
Figure 1.1. Important chemicals based on benzene.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مكتبة أمّ البنين النسويّة تصدر العدد 212 من مجلّة رياض الزهراء (عليها السلام)
|
|
|