


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 29-11-2019
Date: 3-12-2015
Date: 12-7-2018
|
Naming Alkenes
Alkenes are named using a series of rules similar to those for alkanes with the suffix -ene used instead of -ane to identify the functional group. There are three steps to this process.
Step 1
Name the parent hydrocarbon. Find the longest carbon chain containing the double bond, and name the compound accordingly, using the suffix -ene:

Step 2
Number the carbon atoms in the chain. Begin at the end nearer the double bond or, if the double bond is equidistant from the two ends, begin at the end nearer the first branch point. This rule ensures that the double-bond carbons receive the lowest possible numbers.
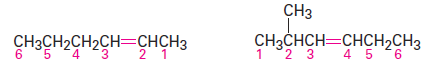
Step 3
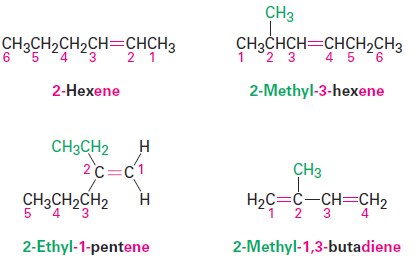
Write the full name. Number the substituents according to their positions in the chain, and list them alphabetically. Indicate the position of the double bond by giving the number of the first alkene carbon and placing that number directly before the parent name. If more than one double bond is present, indicate the position of each and use one of the suffixes -diene, -triene, and so on.
We should also note that IUPAC changed their naming recommendations in 1993 to place the locant indicating the position of the double bond immediately before the -ene suffix rather than before the parent name: but-2-ene rather than 2-butene, for instance. This change has not been widely accepted by the chemical community in the United States, however, so we’ll stay with the older but more commonly used names. Be aware, though, that you may occasionally encounter the newer system.
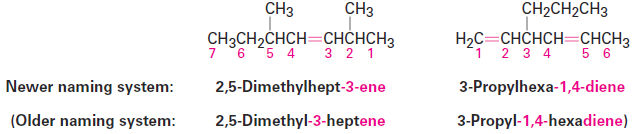
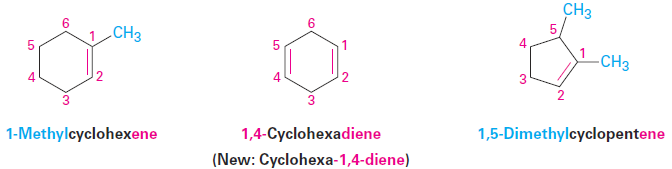
Cycloalkenes are named similarly, but because there is no chain end to begin from, we number the cycloalkene so that the double bond is between C1 and C2 and the first substituent has as low a number as possible. It’s not necessary to indicate the position of the double bond in the name because it’s always between C1 and C2. As with open-chain alkenes, the newer but not yet widely accepted naming rules place the locant immediately before the suffix in a cyclic alkene.
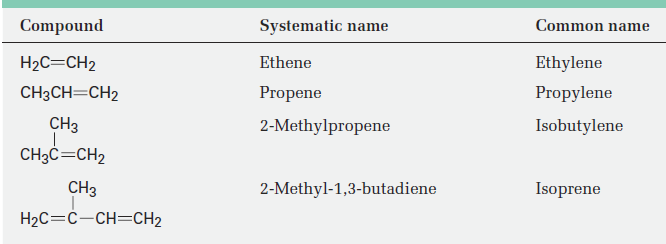
For historical reasons, there are a few alkenes whose names are firmly entrenched in common usage but don’t conform to the rules. For example, the alkene derived from ethane should be called ethene, but the name ethylene has been used for so long that it is accepted by IUPAC. Table 1.1 lists several other common names that are often used and are recognized by IUPAC. Note also that a =CH2 substituent is called a methylene group, a H2C=CH- substituent is called a vinyl group, and a H2C=CHCH2- substituent is called an allyl group.
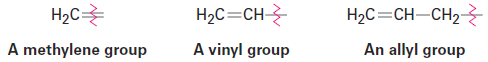
Table 1.1 Common Names of Some Alkenes



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تستعد لإطلاق الحفل المركزي لتخرج طلبة الجامعات العراقية
|
|
|