


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 19-3-2016
Date: 19-3-2016
Date: 19-3-2016
|
The Population Standard Deviation σ
The population standard deviation σ, which is a measure of the precision of the population, is given by the equation
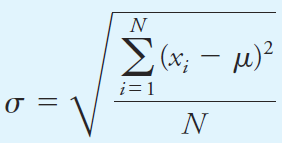
where N is the number of data points making up the population. The two curves in Figure 1.1a are for two populations of data that differ only in their standard deviations. The standard deviation for the data set yielding the broader but lower curve B is twice that for the measurements yielding curve A. The breadth of these curves is a measure of the precision of the two sets of data. Thus, the precision of the data set leading to curve A is twice as good as that of the data set represented by curve B. Figure 1.1b shows another type of normal error curve in which the x axis is now a new variable z, which is defined as
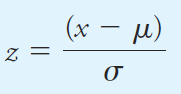
Note that z is the relative deviation of a data point from the mean, that is, the deviation relative to the standard deviation. Hence, when x - μ = σ, z is equal to one; when x - μ = 2σ, z is equal to two; and so forth. Since z is the deviation from the mean relative to the standard deviation, a plot of relative frequency versus z yields a single Gaussian curve that describes all populations of data regardless of standard deviation. Thus, Figure 1.1b is the normal error curve for both sets of data used to plot curves A and B in Figure 1.1a. The equation for the Gaussian error curve is
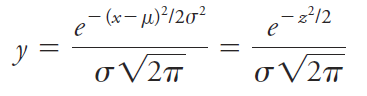
Because it appears in the Gaussian error curve expression, the square of the standard deviation σ2 is also important. This quantity is called the variance A normal error curve has several general properties: (a) The mean occurs at the central point of maximum frequency, (b) there is a symmetrical distribution of positive and negative deviations about the maximum, and (c) there is an exponential decrease in frequency as the magnitude of the deviations increases. Thus, small uncertainties are observed much more often than very large ones.
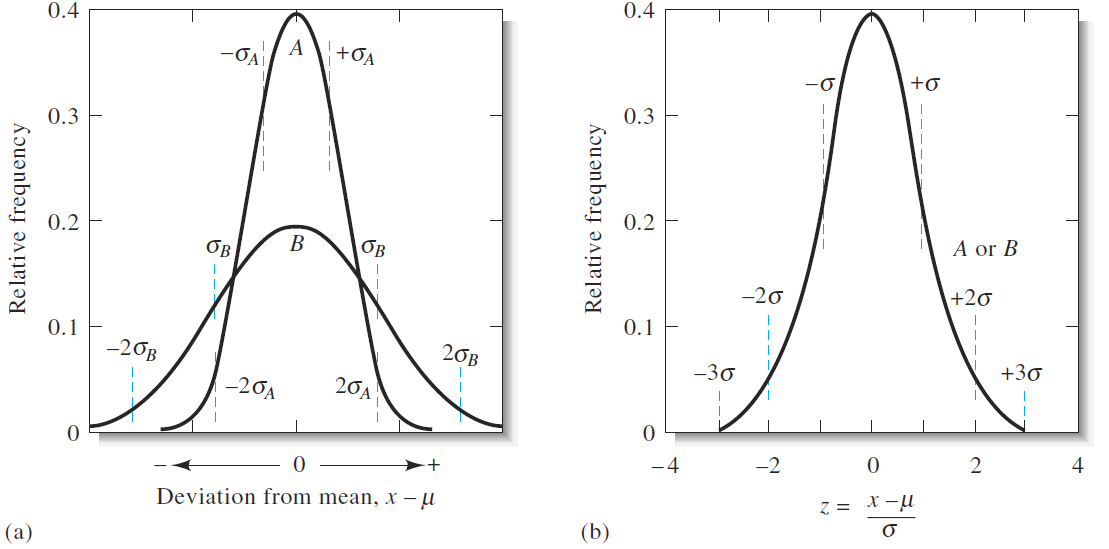
Figure 1.1 Normal error curves. The standard deviation for curve B is twice that for curve A, that is, σB = 2σA. In (a) the abscissa is the deviation from the mean (x – μ) in the units of measurement. In (b) the abscissa is the deviation from the mean in units of s. For this plot, the two curves A and B are identical.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مكتبة أمّ البنين النسويّة تصدر العدد 212 من مجلّة رياض الزهراء (عليها السلام)
|
|
|