


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 23-1-2017
Date: 23-1-2017
Date: 13-11-2020
|
The exterior Schwarzschild solution
Just a few months after Einstein had published his new gravitational theory, the astronomer K Schwarzschild found an exact solution to Einstein's field equation. The so-called Schwarzschild solution is amazingly simple, especially in view of the field equations which are very complicated. However, the Schwarzschild solution is not a degenerated case for over-simplified situations but physically most meaningful. It is this solution by means of which one can explain most general relativistic effects in the planetary system. The reason is that it describes the gravitational field outside of a spherically symmetric body like the planets and the sun.
We start from the spherically symmetric metric:
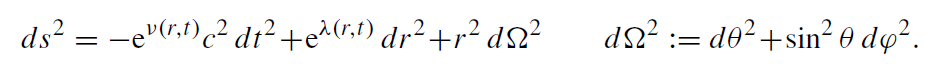 (1.1)
(1.1)
One can now compute the Christoffel symbols, the Riemann tensor, and the Einstein tensor for this ansatz. This can be done by hand, of course. It is more convenient to use computer algebra. For vacuum and Λ = 0, it is relatively simple to find a solution to Gαβ = κTαβ = 0, namely
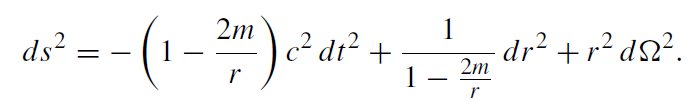 (1.2)
(1.2)
This is the Schwarzschild metric. There is no time dependence although we did allow for that in the ansatz (1.1). The vacuum spacetime structure generated by any spherically symmetric body is static. This applies also for the exterior field of a radially oscillating body. This fact is known as Birkhoff ’s theorem.
The parameter 2m is an integration constant. Its interpretation can be obtained by means of a transition to Newton's theory. It turns out that (G is Newton's gravitational constant and M is the mass of gravitating body)
 (1.3)
(1.3)
This is the Schwarzschild (or gravitational) radius. In this chapter, we distinguish between m and M. In subsequent chapters, it is generally assumed that c = 1 = G. Then, we have m = M. At the Schwarzschild radius rS the metric coefficients become singular. However, this is only a so-called coordinate singularity since the curvature tensor (and therewith physically meaningful quantities like the tidal force) remains finite. We can also see this explicitly when we introduce suitable coordinates, like isotropic coordinates. Therefore we define a new radial coordinate . r as follows:
 (1.4)
(1.4)
Then, the Schwarzschild metric becomes
 (1.5)
(1.5)
In these coordinates, there is only a singularity at . r = 0, which corresponds to r = 0.
As already indicated at the beginning of this section, several experimental verifications of general relativity theory rest on the exterior Schwarzschild solution, namely, to mention only some of the catchwords,
● the gravitational red shift,
● the gravitational deflection of light (→gravitational lensing),
● the general relativistic perihelion and periastron advance, and
● the time delay of radar pulses (the Shapiro effect).
Using additional structure from Einstein's theory, more predictions can be verified:
● the Hulse–Taylor pulsar: emission of gravitational waves,
● the Lense–Thirring effect.
For more details on the experimental verification of Einstein's theory.



|
|
|
|
علامات بسيطة في جسدك قد تنذر بمرض "قاتل"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أول صور ثلاثية الأبعاد للغدة الزعترية البشرية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مكتبة أمّ البنين النسويّة تصدر العدد 212 من مجلّة رياض الزهراء (عليها السلام)
|
|
|