


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 11-3-2021
Date: 26-11-2020
Date: 2-12-2020
|
Calculating the Rotational Inertia
For a continuous distribution of mass the rotational inertia has the sum replaced by an integral, namely
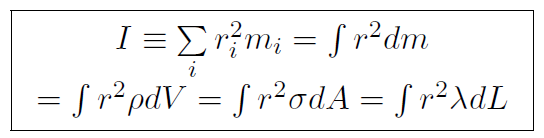
where dm has been replaced by 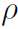 dV or σdA or λdL depending on whether the rigid body is 3-dimensional, 2-dimensional or 1-dimensional. Now when you spin an object, you always spin it about some axis. Take your physics book for example. It is easy to spin about an axis through the center (i.e. center of mass) but more difficult to spin about an axis through the edge of the book. Remember that the rotational inertia I tells us how difficult it is to get something rotating, or spinning, just as ordinary inertia m tells us how difficult it is to get something moving. Thus I is small for the spin axis through the center of the book, but large for an axis through the edge of the book. In the formula for
dV or σdA or λdL depending on whether the rigid body is 3-dimensional, 2-dimensional or 1-dimensional. Now when you spin an object, you always spin it about some axis. Take your physics book for example. It is easy to spin about an axis through the center (i.e. center of mass) but more difficult to spin about an axis through the edge of the book. Remember that the rotational inertia I tells us how difficult it is to get something rotating, or spinning, just as ordinary inertia m tells us how difficult it is to get something moving. Thus I is small for the spin axis through the center of the book, but large for an axis through the edge of the book. In the formula for 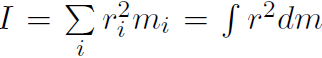 then r will always be measured from the rotation axis. A very handy formula which helps a lot in calculating I is the famous parallel axis theorem,
then r will always be measured from the rotation axis. A very handy formula which helps a lot in calculating I is the famous parallel axis theorem,
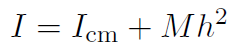
where I is the rotational inertia about an axis located a distance h from the center of mass and parallel to a line through the center of mass. M is the total mass of the whole rigid body. Let's now look at some examples of how to calculate I.
Example A rod of length L and negligible mass has a dumbbell of mass m located at each end. Calculate the rotational inertia about an axis through the center of mass (and perpendicular to the rod).
Solution Each dumbbell is a discrete mass and so we use
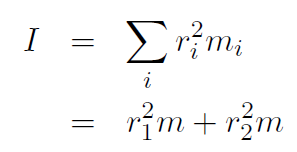
where there are only two terms because there are only two dumbbells, and also m1 = m2 ≡ m. Now 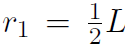 and
and 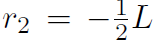 giving
giving
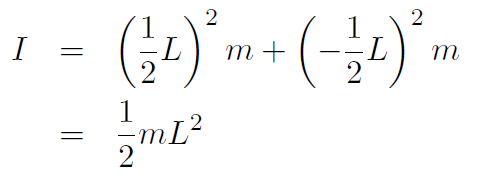
Example Repeat the previous example for an axis through one of the dumbbells (but still perpendicular to the rod).
Solution Now we have
r1 = 0 and r2 = L giving
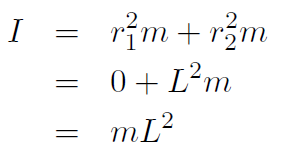
Example Repeat the previous example using the parallel axis theorem.
Solution The parallel axis theorem is I = Icm +Mh2 where the total mass if M = 2m and h is the distance from the center of mass to the rotation axis. Thus h = L/2 giving
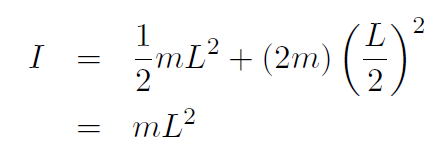
This is the same as before and so we have good reason to believe that the parallel axis theorem is true.
Example Calculate the rotational inertia of a thin uniform rod of mass M and length L about an axis through the center of the rod (and perpendicular to its length).
Solution Let the linear mass density of the rod be 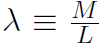 . Then (with dr = dL)
. Then (with dr = dL)
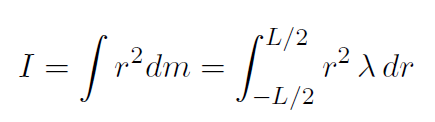
where the integration limits are –L/2 to L/2 because the axis is through the center of the rod. The rod is uniform which means λ is constant and can be taken outside the integral to give
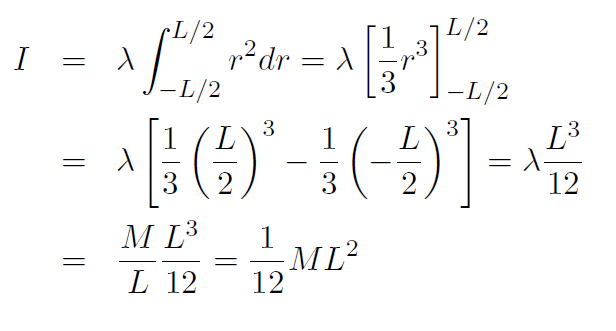
Example Repeat the previous example for an axis through one end of the rod.
Solution Now we have
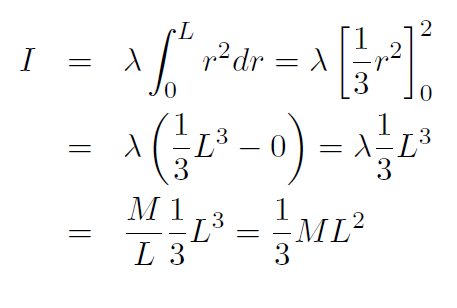
Example Repeat the previous example using the parallel axis theorem.
Solution
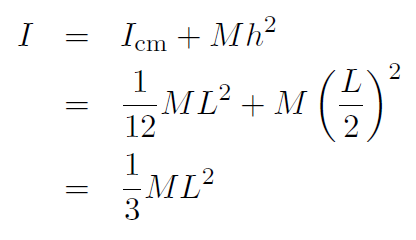



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ووفد من جامعة البصرة يبحثان سبل تعزيز التعاون المشترك
|
|
|