
Collisions that Conserve Momentum and Energy
 المؤلف:
E. R. Huggins
المؤلف:
E. R. Huggins
 المصدر:
Physics 2000
المصدر:
Physics 2000
 الجزء والصفحة:
327
الجزء والصفحة:
327
 26-11-2020
26-11-2020
 1899
1899
Collisions that Conserve Momentum and Energy
When a bullet plows into a block of wood, a considerable amount of energy goes into deforming the wood and bullet. On the other hand if two hardened steel ball bearings collide, almost all the energy stays in the form of kinetic energy of the particles and very little is “lost” as heat, sound, and the deformation of the objects. When no energy is lost this way, we say that the collision is elastic. If energy is lost, then the collision is called inelastic.
On an atomic and subatomic scale we do not have the usual sound and friction, and small deformations may not be allowed. In these circumstances there is no way for energy to become “lost” and the resulting collisions are truly elastic. Thus in the study of the collisions of atomic and subatomic particles, we have examples where both energy and linear momentum are conserved.
Figure (1), shows the track of a proton as it moves through a hydrogen bubble chamber. The incoming track ends when the proton strikes a hydrogen nucleus (another proton) that is part of the liquid hydrogen. Three dimensional stereoscopic photographs show that the two protons recoil from each other at an angle of 90°. Here we are looking at the behavior of matter on a subatomic scale where Newtonian mechanics does not apply, and we would like to find out what we can learn from this collision.
Does this photograph show us that momentum and energy are still conserved on the subatomic scale? To find out we will analyze the collision of larger objects like steel ball bearings, where momentum is conserved and energy nearly so, and see if the results explain what we see in Figure (1).
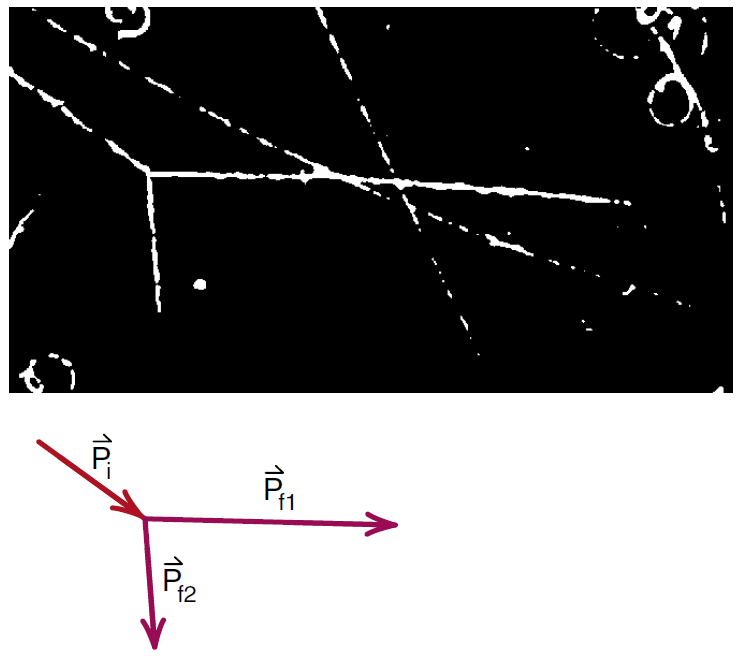
Figure 1:An incoming proton collides with a proton at rest. The two protons recoil at right angles.
 الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


